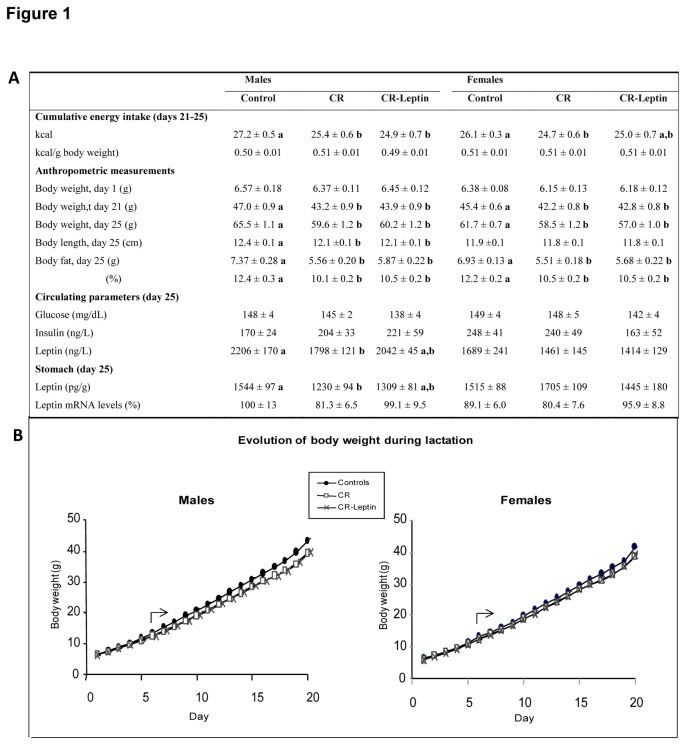
Figure 1. Offspring parameters.
A. Energy intake, anthropometric measurements, circulating parameters and leptin mRNA and protein levels in stomach in the offspring of rats with free access to standard chow diet (control), the offspring of 20% calorie restricted dams during the first 12 days of pregnancy (CR), and CR rats daily supplemented with physiological doses of leptin throughout lactation (CR-Leptin). Cumulative energy intake (from postnatal day 21 to 25) was expressed in kcal, and also referred to body weight and expressed in kcal/g. Body weight was measured on postnatal days 1, 21 and 25. The other parameters were determined on day 25. Leptin mRNA levels in stomach were measured by qRT-PCR and expressed as a percentage of the value of control male rats. Leptin levels in stomach were quantified by ELISA and expressed in pg/g tissue. Data are mean ± S.E.M. For cumulative food intake, body weight at different days, body length and body fat content, n = 16-17; for mRNA analysis, n = 10-11; for circulating parameters, n = 6-8. Each group is made up of animals coming from at least six different litters. Statistics: in case of interaction within each sex, data not sharing a common letter (a and b) are significantly different (a≠b) (p < 0.05; LSD post hoc one-way ANOVA test). B. Evolution of body weight during lactation. The arrow indicates the starting point of significant effects of maternal caloric restriction during gestation on body weight in male and female offspring (CR≠Controls; CR-Leptin≠Controls; p < 0.05; LSD post hoc one-way ANOVA test).