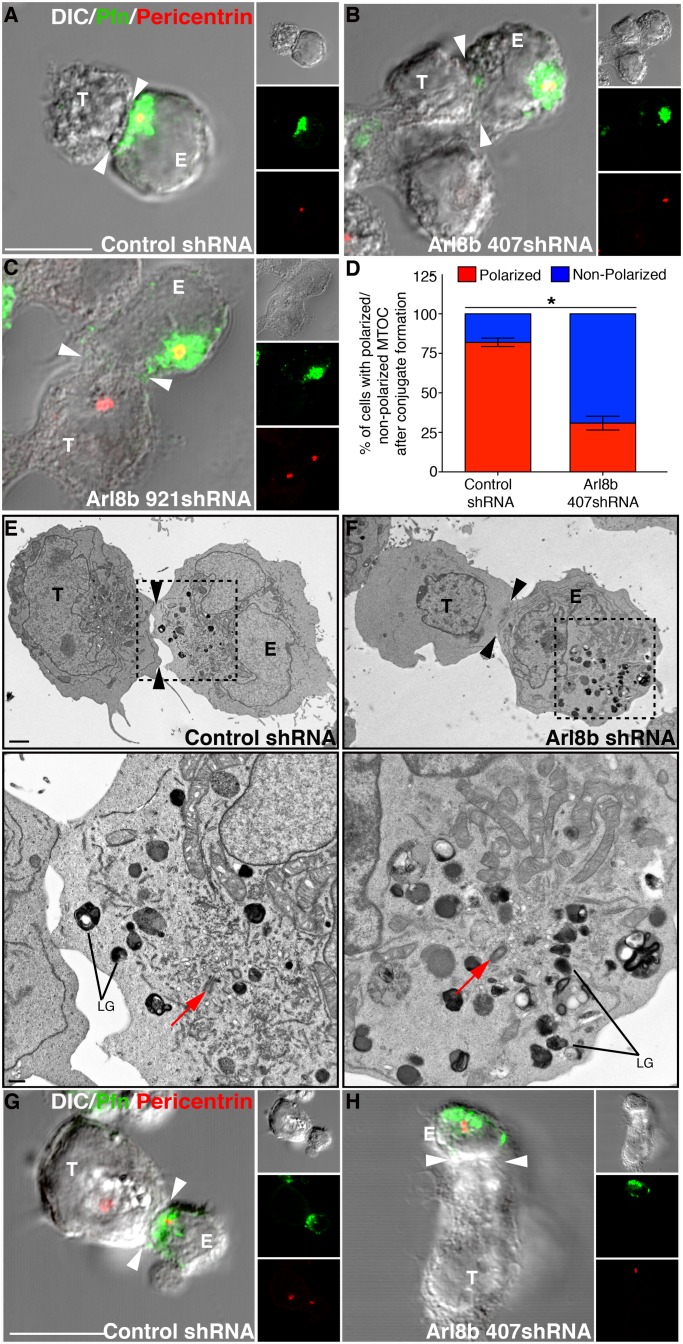
FIGURE 4:
MTOC polarization to the immune synapse is inhibited in Arl8b-silenced NK cells. (A–C) Loss of MTOC polarization upon Arl8b silencing. Confocal analysis was performed on YT-Indy cells (effector) stably transduced with control shRNA or Ar8b-specific shRNA (407 and 921) and mixed with 721.221 cells (target) for 20 min at the E:T ratio of 2:1. Conjugates were fixed, and lytic granules were stained using anti-perforin antibody (green); the MTOC was determined based on pericentrin staining (red). Immune synapse is marked by white arrowhead. (D) Percentage of MTOC (marked by pericentrin staining) polarization in control vs. Arl8b-silenced-YT-Indy cells. Bar graph, mean ± SD of three independent experiments; at least 50 conjugates were evaluated in each experiment. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (*p < 0.05 by Student's t test) as compared with control. (E, F) Transmission electron microscopy of control shRNA– or Arl8b shRNA–transduced YT-Indy cells (E) incubated with 721.221 target cells (T). To better highlight the position of lytic granules (LGs) and MTOC (red arrow) in control vs. Arl8b-silenced NK cell–721.221 conjugates, the boxed area was magnified and is shown at the bottom. Black arrowheads indicate an immune synapse. Scale bar, 2 μm (top) and 500 nm (bottom). The analysis is based on evaluation of at least five conjugates in three separate experiments. (G, H) Control siRNA– and Arl8b siRNA–treated primary human NK cells (effector) were mixed with 721.221 cells (target) for 20 min at the E:T ratio of 2:1. Conjugates were fixed, costained for perforin (green) and pericentrin (red), and analyzed by confocal microscopy.