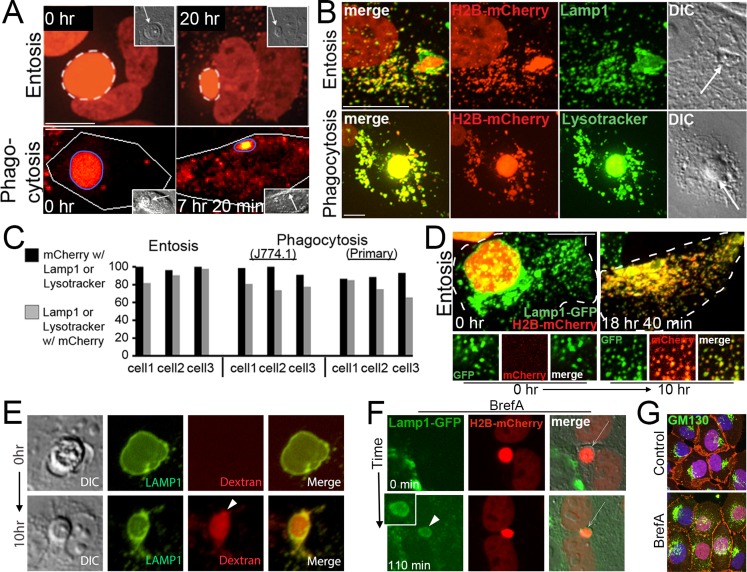
FIGURE 3:
Phagosomes and entotic vacuoles undergo fission. (A) mCherry fluorescence from an entotic corpse expressing H2B-mCherry (top) or an apoptotic corpse expressing H2B-mCherry (bottom) appears as puncta in the cytoplasm of engulfing cells (right) as entotic vacuoles (white dashed circle) and phagosomes (blue circle) shrink over time. Images from time-lapse analysis show mCherry fluorescence (red); insets, DIC; arrows indicate corpses. Note that entotic engulfing cell in top is binucleate and also expresses H2B-mCherry. Bars, 10 μm. See Supplemental Videos S1 and S2. (B) mCherry puncta colocalize with Lamp1-GFP in entotic cells (top) and LysoTracker in primary macrophages (bottom). Maximum projection images of mCherry fluorescence (red), Lamp1-GFP and LysoTracker green (green), and merged and DIC images as indicated; arrows indicate cell corpses. Bars, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of colocalization between mCherry and Lamp1 or LysoTracker in individual phagocytic or entotic engulfing cells. Black bars, percentage of mCherry puncta that colocalize with Lamp1 or LysoTracker; gray bars, percentage of Lamp1 or LysoTracker vesicles that colocalize with mCherry. Percentages for three individual engulfing cells for entosis (MCF10A) or phagocytosis (J774.1 and primary macrophages) are shown. For entosis, cell 1, n = 124 vesicles (black bar) and 137 vesicles (gray bar); cell 2, n = 132, 137; and cell 3, n = 131, 125. For J774.1 phagocytosis, cell 1, n = 66, 83; cell 2, n = 54, 76; and cell 3, n = 55, 67. For phagocytosis with primary macrophages, cell 1, n = 96, 100; cell 2, n = 174, 171; cell 3, n = 157, 143. (D) Corpse-derived mCherry fluorescence redistributes from the entotic vacuole to the lysosome network of the engulfing cell. Maximum projections from confocal time-lapse analysis of a Lamp1-GFP–expressing MCF10A cell with an engulfed entotic corpse expressing H2B-mCherry. Note that Lamp1-GFP–labeled lysosomes acquire red fluorescence over time as entotic vacuole undergoes fission. Top, merged green and red fluorescence of whole cell outlined with hatched white line. Bottom, individual and merged fluorescent channels at time 0 and 10 h for an area of cell cytoplasm. Bar, 10 μm. See Supplemental Video S3. (E) Entotic vacuole, labeled with Lamp1-GFP (green), accumulates 10-kDa red fluorescent dextran (arrowhead) from media over the course of 10 h as the vacuole shrinks in size. Also see Supplemental Figure S5a. (F) An entotic vacuole (arrow) in brefeldin A–treated cells fuses with Lamp1-GFP–labeled lysosomes (green) after polyethylene glycol (PEG)–initiated cell fusion. Arrowhead indicates Lamp1-GFP accumulation at entotic vacuole. Time indicates minutes after cell fusion. Also see Supplemental Figure S5, b and c. (G) Brefeldin A treatment as in F disrupts the Golgi, as shown by GM130 immunostaining (green) in mixed cultures used for cell fusion in F. β-Catenin immunostaining and H2B-mCherry are shown in red. Note that the H2B-mCherry–expressing cells used in this experiment do not express Lamp1-GFP (green), so cells with red nuclei show only GM130 immunofluorescence in the green channel, whereas cells without red nuclei show GM130 immunofluorescence and Lamp1-GFP fluorescence in the green channel.