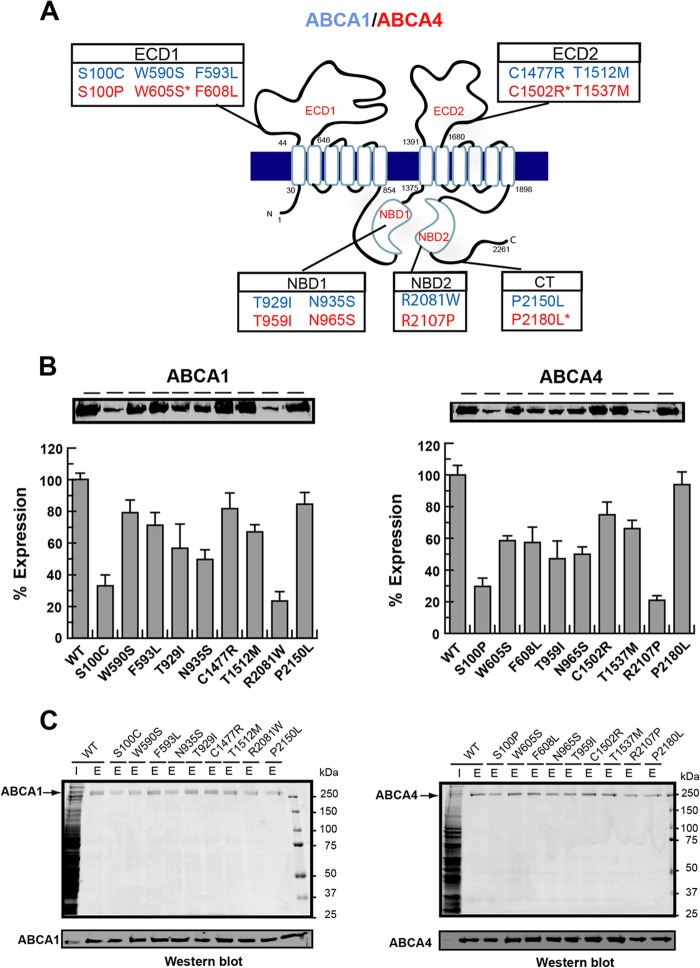
FIGURE 6.
Expression and purification of ABCA1 and ABCA4 disease-associated mutants. A, topological diagram of human ABCA1 and ABCA4 showing the position of the nine ABCA1 mutants associated with Tangier disease mutants (blue) and related ABCA4 mutants, many of which are associated with Stargardt disease (red) in relation to the various domains (exocytoplasmic domains ECD1 and ECD2, nucleotide binding domains NBD1 and NBD2, and C-terminal domain (CT)). Some disease alleles such as W590S, C1477R, and P2150L (ABCA1) have conserved residues in ABCA4, but mutations in these positions in ABCA4 have yet to be linked to Stargardt disease. B, expression profile of ABCA1 and ABCA4 disease-associated mutants relative to the WT protein. Proteins were expressed in HEK293T cells, and extracts were resolved by SDS-gel electrophoresis. An example of a Western blot labeled with the Rho1D4 antibody is shown along with quantitation from three independent experiments. C, purification of mutants on a Rho1D4 immunoaffinity matrix. Upper panel is a Coomassie Blue-stained gel of the WT extract (I) and 1D4 peptide-eluted protein (E). Lower panel is a Western blot labeled with the Rho1D4 antibody.