FIGURE 5.
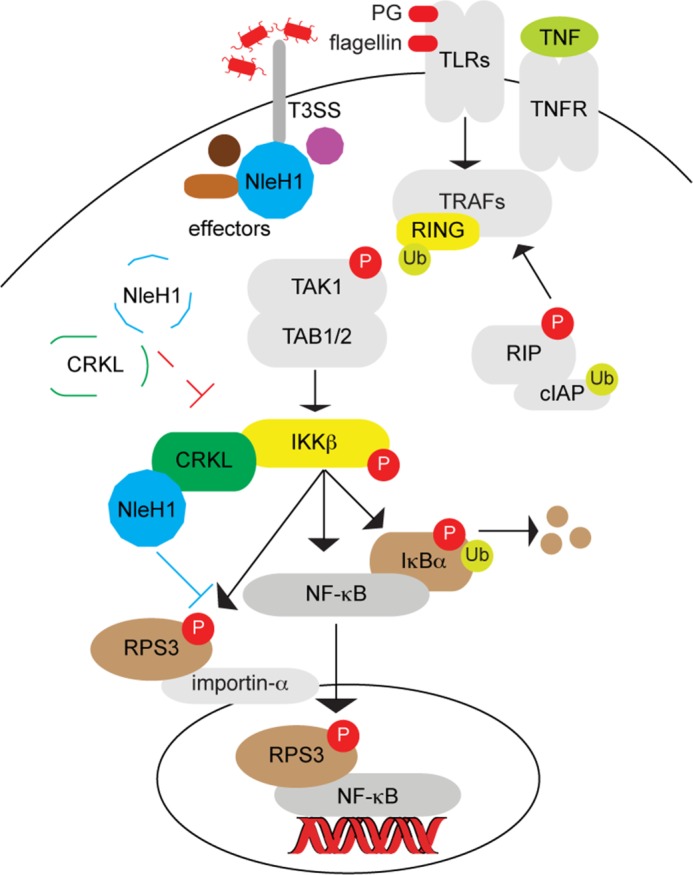
Model illustrating the potential role of CRKL in recruiting NleH1 to inhibit RPS3/NF-κB signaling during A/E pathogen infection. During A/E pathogen infection, NleH1 is injected into host cells through the T3SS and then interacts with CRKL. CRKL interacts with IKKβ and may recruit NleH1 to the RPS3-NF-κB complex, where NleH1 can then inhibit RPS3 phosphorylation. In the absence of CRKL (indicated by dashed lines), NleH1 is not recruited to the IKKβ-RPS3 complex and fails to block RPS3 nuclear translocation. PG, peptidoglycan; TLRs, Toll-like receptors; TNFR, TNF receptor; TRAF, TNF receptor-associated factor; Ub, ubiquitin; RIP, receptor-interacting protein; cIAP, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein.
