Fig. 6.
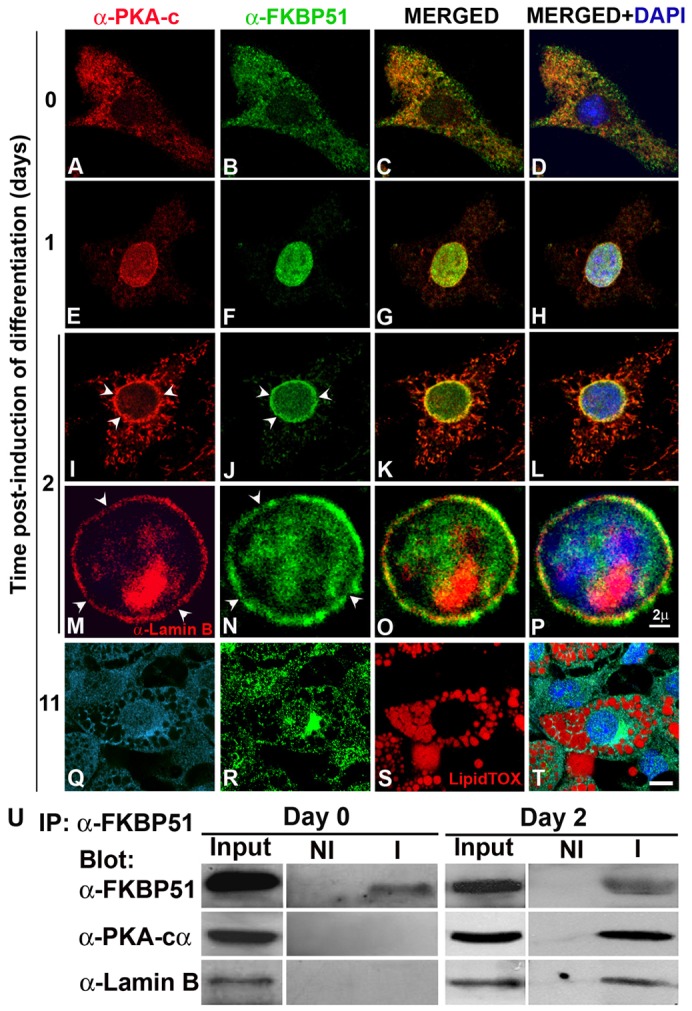
FKBP51 and PKA-cα transiently colocalize in the nuclear lamina at the onset of adipocyte differentiation. (A–T) 3T3-L1 preadipocytes grown on coverslips were induced to differentiate for the indicated periods of time and subcellular localization of PKA-cα and FKBP51 was assessed by IIF and confocal microscopy. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. For M, O and P, IIF was performed using anti-lamin B to label the nuclear lamina. Arrowheads in M and N indicate loss of lamin B or FKBP51 in the nuclear rim, respectively. (Q–T) PKA-cα is shown in light blue (Q) to distinguish it from the nucleus stained with DAPI (blue) and the lipid vesicles were stained with LipidTOX (red; S). Scale bars: 2 µm (A–P); 5 µm (Q–T). (U) FKBP51 was immunoprecipitated from 3T3-L1 cells prior to (day 0) and 2 days after induction of differentiation, and immunoprecipitated complexes were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. NI, non-immune antibody; I, immune antibody. Results are representative of four independent experiments.
