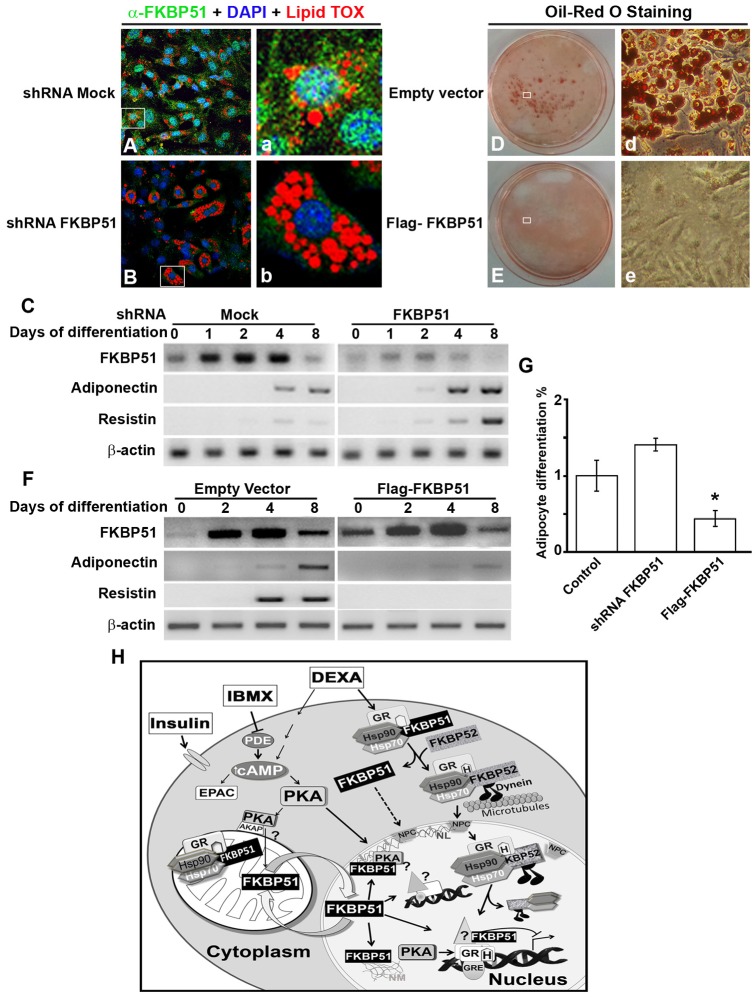
Fig. 8.
FKBP51 restrains differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Plasmids with mock shRNA or shRNA specific for FKBP51 were transfected in 3T3-L1 cells, and 48 hours later cells were induced to differentiate. Adipogenesis was evaluated by IIF using LipidTOX to stain vesicles containing lipids (A,B), and by evaluating mRNA for FKBP51, adiponectin and resistin (C). 3T3-L1 cells were transfected with empty vector or FLAG-FKBP51, and 24 hours later cells were induced to differentiate and adipocyte differentiation was evaluated by Oil Red O staining (D,E), and by detecting mRNA for FKBP51, adiponectin and resistin (F). β-Actin was used as a control of loading in C and F. (G) Fold change in the percentage of cells that differentiated into adipocytes for control cells, and 3T3-L1 cells in which FKBP51 was knocked down (shRNA FKBP51) or overexpressed (Flag-FKBP51), *P<0.01. (H) Model of FKBP51 activity in adipocyte differentiation. In the adipogenic cocktail MDI, IBMX and DEXA are responsible for FKBP51 nuclear translocation. IBMX inhibits the phosphodiesterase (PDE) increasing intracellular cAMP that activates PKA, and induces PKA-cα and mitochondrial FKBP51 nuclear translocation, where they mainly colocalize in the nuclear lamina (NL). In the nucleus, FKBP51 is retained by its interaction with the nuclear matrix (NM) and chromatin, regulating GR-target genes, and possibly other targets.