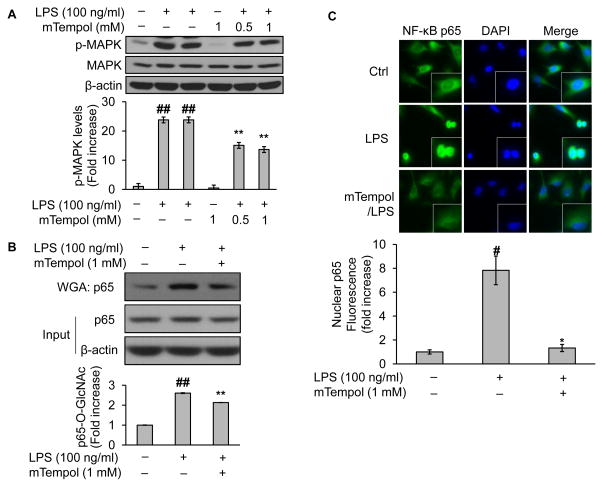
Fig. 7.
Scavenging superoxide obliterates the O-GlcNAc modification and nucleus translocation of NF-κB/p65 in LPS-challenged endothelial cells. BAEC were pretreated either with vehicle (culture medium) or mTempol (up to 1mM, a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant with superoxide scavenging properties) for up to 1 h followed by incubation with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 1 h. The treated cells were subjected to (A) assessment of the role of superoxide scavenger on LPS-induced MAPK activation by Western blot; (B) Western blotting of proteins either from WGA-enriched O-GlcNAc modified proteins or whole cell lysates (to assess protein input as a loading control); (B) immunofluorescent staining of NF-κB or DAPI with a kit including ProLong® Gold and SlowFade® Gold Antifade. The secondary antibody was conjugated with a fluorescent green dye (Alexa Fluor 488). Nuclear p65 fluorescence was quantified. All images shown are representative of three independent experiments. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (n=3). #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 compared to the vehicle-treated control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared to the LPS-only group.