Figure 4.
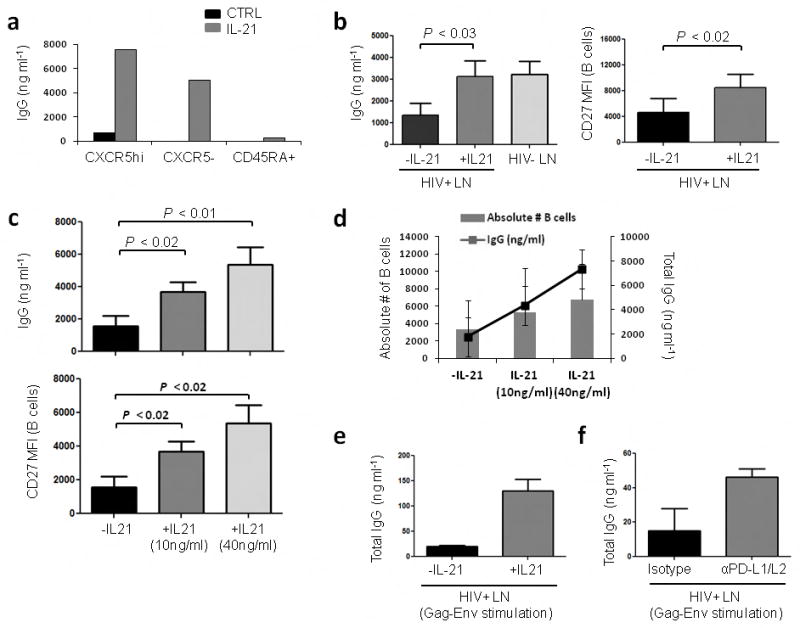
Supplementation with IL-21 restores IgG production in co-cultures from HIV-infected LNs. (a) Representative graph depicting IgG levels in co-cultures of GC-enriched B cells with CXCR5hi, CXCR5− or CD45RA+ T cell subsets in the presence of SEB with or without recombinant human IL-21 (10 ng ml−1) after 7 d. (b) Increase in IgG production and CD27 MFI on B cells when cocultures of Tfh and GC-enriched B cells from HIV+ LNMCs are supplemented with IL-21 (n=5). (c) Dose dependent effect of IL-21 on IgG production and CD27 MFI on B cells (n=4). (d) Dose dependent effect of IL-21 supplementation on the absolute number of B cells and IgG production in co-cultures of Tfh and GC-enriched B cells from HIV+ LNMCs (n=4) after 7 d. (e) Effect of IL-21 supplementation on total IgG levels following antigen specific stimulation by culturing Tfh cells and GC-enriched B cells in the presence of primed monocytes after 7 d. (n=2). (f) Effect of PD-L1/L2 blocking on IgG production in cocultures of Tfh cells and GC-enriched B cells in the presence of primed monocytes after 7 d (n=2).
