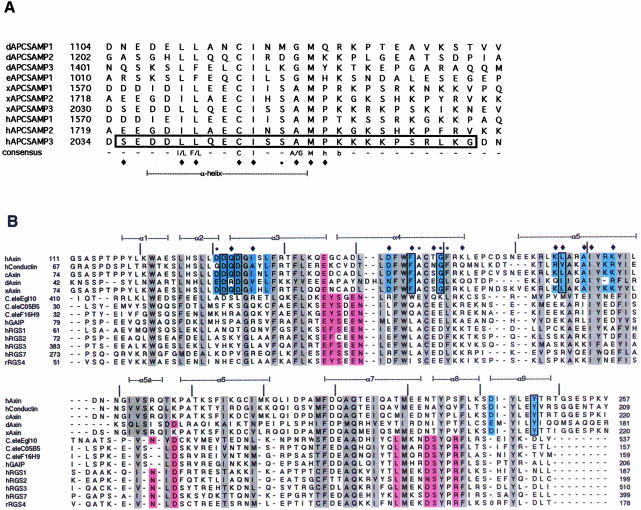
Fig. 3. Conservation of SAMP repeats and RGS domains. (A) Alignment of the SAMP repeats of Drosophila APC (dAPC), Drosophila APC2 (eAPC), Xenopus and human APC. Starting residue numbers for within the full-length proteins are indicated. The SAMP3 sequence used in crystallization is boxed. Residues that contact Axin-RGS in the RGS–SAMP3 complex structure are indicated by a diamond (contacts by side chain atoms) or an asterisk (contacts by main chain atoms only) below the alignment. A consensus sequence is given (h, hydrophobic; b, basic), and the residues that form the α-helical portion of the peptide are indicated. (B) Structure-based alignment of Axin-RGS and RGS4 with other RGS family members. Conserved hydrophobic core residues are highlighted in gray, residues determined to contact Giα in the RGS4–Giα complex structure (Tesmer et al., 1997) are in pink. Conserved Axin subfamily residues are light blue. Residues that contact SAMP3 in the RGS–SAMP3 complex structure are indicated by symbols above the alignment, as in (A). Those residues changed in human Axin in the mutagenesis experiments are boxed. Secondary structure elements observed in Axin-RGS are indicated above the alignment (α1–α9), and tick marks indicate every 10 residues in human Axin. Axin family members shown are: human Axin (crystal structure in this paper, DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession No. AAC51624), human conductin (NM_004655), chicken Axin (AF009012), Drosophila Axin (AF086811) and Xenopus Axin (AF097313). Other RGS family members are Caenorhabditis elegans Egl10 (CEU32326), C05B5 (Z32679) and F16H9 (Z50005), human GAIP (NM_005873), human RGS 1 (NM_002922), 2 (NM_002923), 3 (HSU27655) and 7 (U32439) and rat RGS4 (AF117211).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.