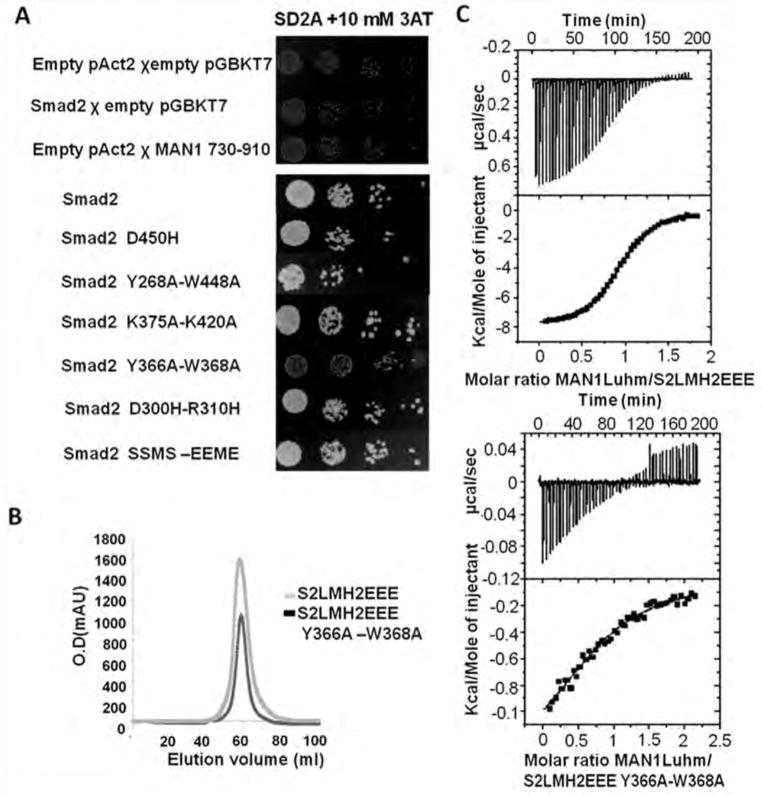
Fig 2.
Tyr366 and Trp368 in the Smad2 MH2 domain are involved in binding to MAN1. (A) Yeast two-hybrid assay results for binding of MAN1 fragments, which included fragments containing amino acid residues 730 to 910 and full-length Smad2 variants. Top panel, protein-coding or empty plasmids were used to transform yeast for the indicated control experiments. Bottom panel, results for interactions between the MAN1 fragments and the indicated wild-type and mutant Smad2 constructs. Physical interaction between a Smad2 variant and the Man1 fragment activated expression of HIS3, which enabled yeast cell growth. N=2 independent biological replicates. (B) Chromatography elution profiles of the two Smad2 fragments S2LMH2EEE and S2LMH2EEE W366A-Y368A. N=3 independent biological replicates. (C) Representative binding curves obtained by ITC for the MAN1 fragment containing amino acid residues 755 to 911 (MAN1Luhm) added to a phosphomimetic mutant of the MH2 domain of wild-type Smad2 (S2LMH2EEE, left), and its Y366A-W388A mutant (right). Fitting these curves yielded the Kd values in Table 1.