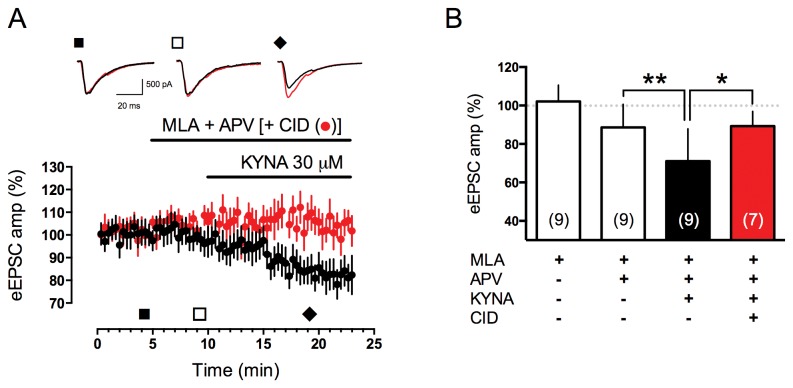
Figure 4. KYNA reduces eEPSCs amplitude at CA3-CA1 synapse in a GPR35 dependent manner.
A) Time course of KYNA-induced decrease in eEPSC amplitude, normalized to pre-application values, in the presence of D-APV and MLA (50 µM and 100 nM, respectively; black dots), or D-APV, MLA and CID (10 µM; red dots). Sample traces are shown on top. B) Bar graph shows maximal effect of KYNA and its antagonism by CID. The effect of KYNA was statistically significant compared to pre-application level (third vs second column, One-Way ANOVA for repeated measures, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). Preincubation with CID was able to prevent the effect of KYNA (fourth vs third column, two-way t-test for unpaired sets of data).