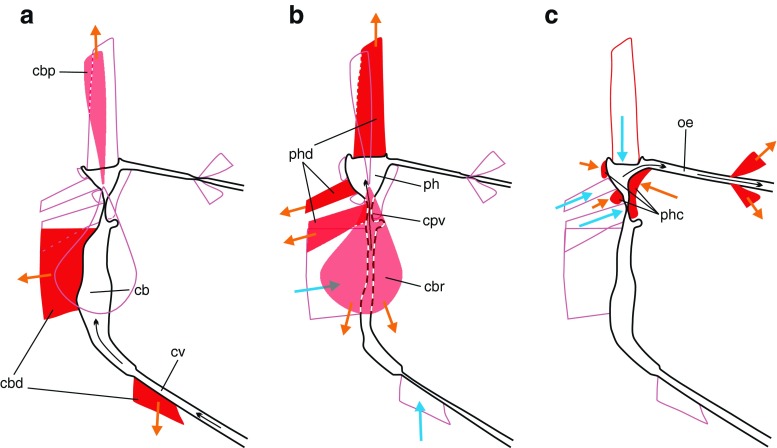
Fig. 5.
Three-phase suction pump of Prosoeca sp. based on microCT scans. Contracting muscles are drawn in red with orange arrows; relaxing muscles are hollow with blue arrows. a Cibarial dilator muscles open the cibarial valve and suck nectar into the cibarium. b Pharyngeal dilators pump nectar through the cibarial–pharyngeal valve into the pharynx. In phase A and B, the cibarial protractor and retractor (light red) work as antagonists to the main dilator muscles to hold the pump stationary. c Pharyngeal compressor muscles push the nutrition into the oesopharynx, and the posterior dilator muscles open the oesopharyngeal valve. Cuticle elasticity of both pump chambers provides restoration force to reset the suction pump for the next food intake phase. Cb cibarium, cbd cibarial dilator, cbp cibarial protractor, cbr cibarial retractor, cpv cibarial–pharyngeal valve (true mouth), cv cibarial valve (functional mouth), oe oesophagus, ph pharynx, phc pharyngeal compressor, phd pharyngeal dilator