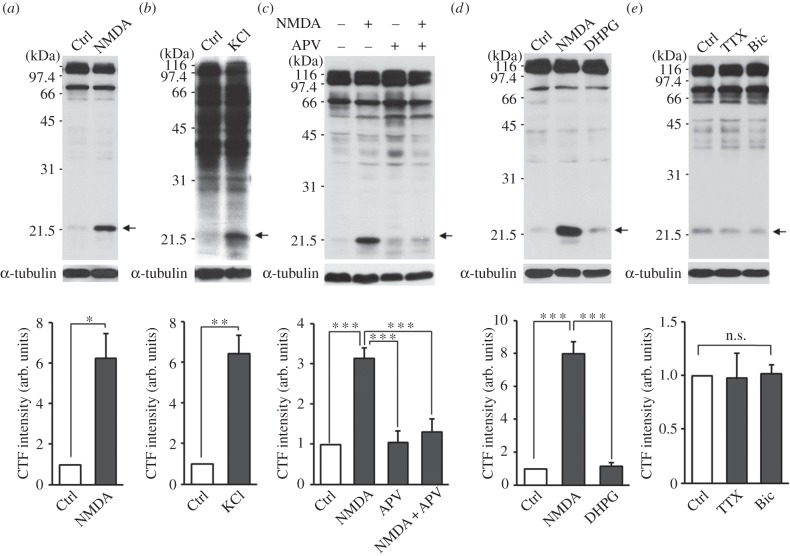
Figure 1.
NGL-3 cleavage requires NMDAR activation, but not mGluR activation or chronic changes in neuronal activity. (a) NMDA treatment of cultured neurons induces NGL-3 cleavage. Rat hippocampal neurons at days in vitro (DIV) 18–21 were stimutated with NMDA (20 µM, 3 min), followed by direct lysis of the neurons in SDS-PAGE sample buffer and immunoblotting with NGL-3 antibodies (#1948). For quantitative analyses, the intensity of the 22 kDa band (indicated by an arrow) was normalized to that of α-tubulin and compared with other normalized intensities. The bar graphs represent mean ± s.e.m.; n = 3, *p < 0.05, Student's t-test. (b) KCl-dependent depolarization induces NGL-3 cleavage. Rat hippocampal neurons at DIV 18–21 were stimutated with KCl (50 mM, 5 min) followed by immunoblotting; n = 4, **p < 0.01, Student's t-test. (c) NMDA receptor activation is required for NMDA-induced NGL-3 cleavage. Rat hippocampal neurons pretreated with APV (NMDA receptor antagonist; 50 µM, 30 min) were stimulated with NMDA (20 µM, 3 min) and analysed by immunoblotting; n = 5, ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA. (d) Activation of NMDA receptors, but not mGluRs, leads to NGL-3 cleavage. Rat hippocampal neurons at DIV 18–21 were stimutated with NMDA (20 µM, 3 min) or DHPG (group I mGluR agonist; 50 µM, 30 min); n = 3, ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA. (e) Chronic inhibition or activation of cultured neurons does not induce NGL-3 cleavage. Rat hippocampal neurons at DIV 18–21 were stimutated with tetrodotoxin (TTX; 1 µM for 48 h) or bicuculline (Bic; 10 µM for 36 h); n = 3, n.s., not significant, one-way ANOVA. arb. units, arbitrary units; Ctrl, control.