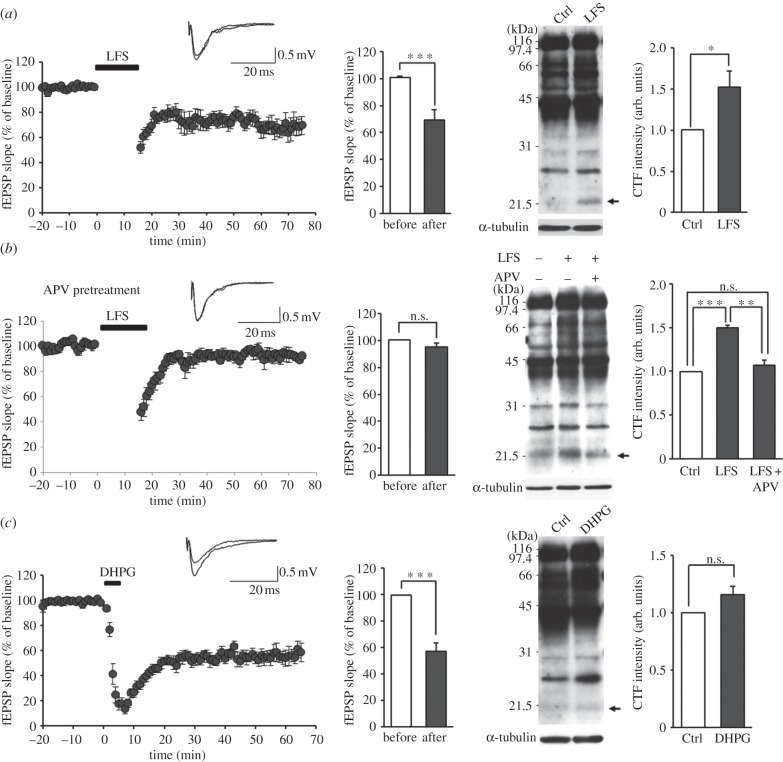
Figure 2.
LTD-inducing low-frequency stimulation induces NGL-3 cleavage in hippocampal slices. (a) Low-frequency stimulation in slices induces NGL-3 cleavage. The Schaffer collateral pathway of acute mouse hippocampal slices (3–4 weeks old) was stimulated by low-frequency stimuli (LFS, 1 Hz, 15 min), followed by immunoblot analysis of hippocampal lysates using NGL-3 antibodies (#2020). The induction of LFS-LTD was confirmed by comparing the average slope of fEPSPs (field excitatory postsynaptic potentials) before stimulation with that during the last 5 min of recording. The top panel shows sample EPSPs. The bar graphs represent mean ± s.e.m; n = 4 slices from three mice, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, Student's t-test. (b) NMDA receptor activation is required for LFS-induced cleavage of NGL-3-CTF. Acute mouse hippocampal slices (3–4 weeks old) were incubated with APV (NMDA receptor antagonist; 50 µM) throughout the experiment starting from 20 min before LFS, followed by immunoblot analysis of hippocampal lysates. The blockade of LFS-LTD was confirmed by comparing the average slope of fEPSPs before stimulation with that during the last 5 min of recording; n = 3 slices from two mice, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n.s., not significant, Student's t-test and one-way ANOVA. (c) DHPG treatment in slices does not induce NGL-3 cleavage. Acute mouse hippocampal slices (3–4 weeks old) were stimulated with DHPG (50 µM, 5 min), followed by immunoblot analysis of hippocampal lysates. The induction of mGluR-LTD by DHPG was confirmed by comparing the average slope of fEPSPs before stimulation with that during the last 5 min of recording. The top panel shows sample EPSPs; n = 6 slices from four mice, ***p < 0.001, n.s., not significant, Student's t-test. Ctrl, unstimulated control slices.