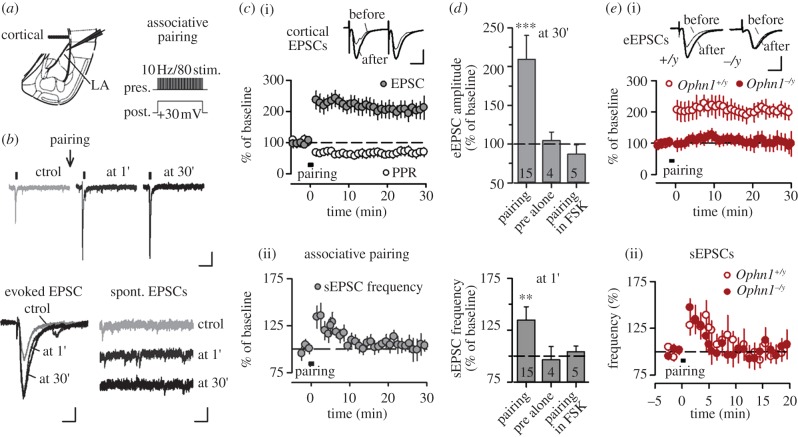
Figure 2.
Constitutive lack of OPHN1 abolishes PKA-dependent presynaptic LTP downstream of AC activation. (a) Scheme of the experimental preparation and pairing protocol. Cortico-LA LTP was induced by pairing postsynaptic depolarization (8 s, +30 mV) with presynaptic stimulation (80 stimuli at 10 Hz). (b) Induction of presynaptic cortico-LA LTP leads to a persistent increase in EPSC amplitude and to a transient increase of sEPSC frequency. Scale bars, 50/50/25 pA and 300/5/25 ms (top/left/right panels). (c(i)) Presynaptic cortico-LA LTP is associated with a change in the PPR. Scale bars: 50 pA and 15 ms. (c(ii)) Associative pairing induces a transient increase of sEPSC frequency. (d) Characterization of pairing-induced cortico-LA LTP of the eEPSC (30 min time point) and the potentiation of sEPSC frequency (1 min time point). Both forms of plasticity are sensitive to pre-incubation with forskolin, and require coincident pre- and postsynaptic activity. See text for further details. Number of recorded cells is indicated. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. (e(i)) LTP induction in Ophn1+/y and Ophn1−/y animals. Scale bars, 50 pA and 5 ms. (e(ii)) LTP induction in both Ophn1+/y and Ophn1−/y animals leads to a transient increase in sEPSC frequency.