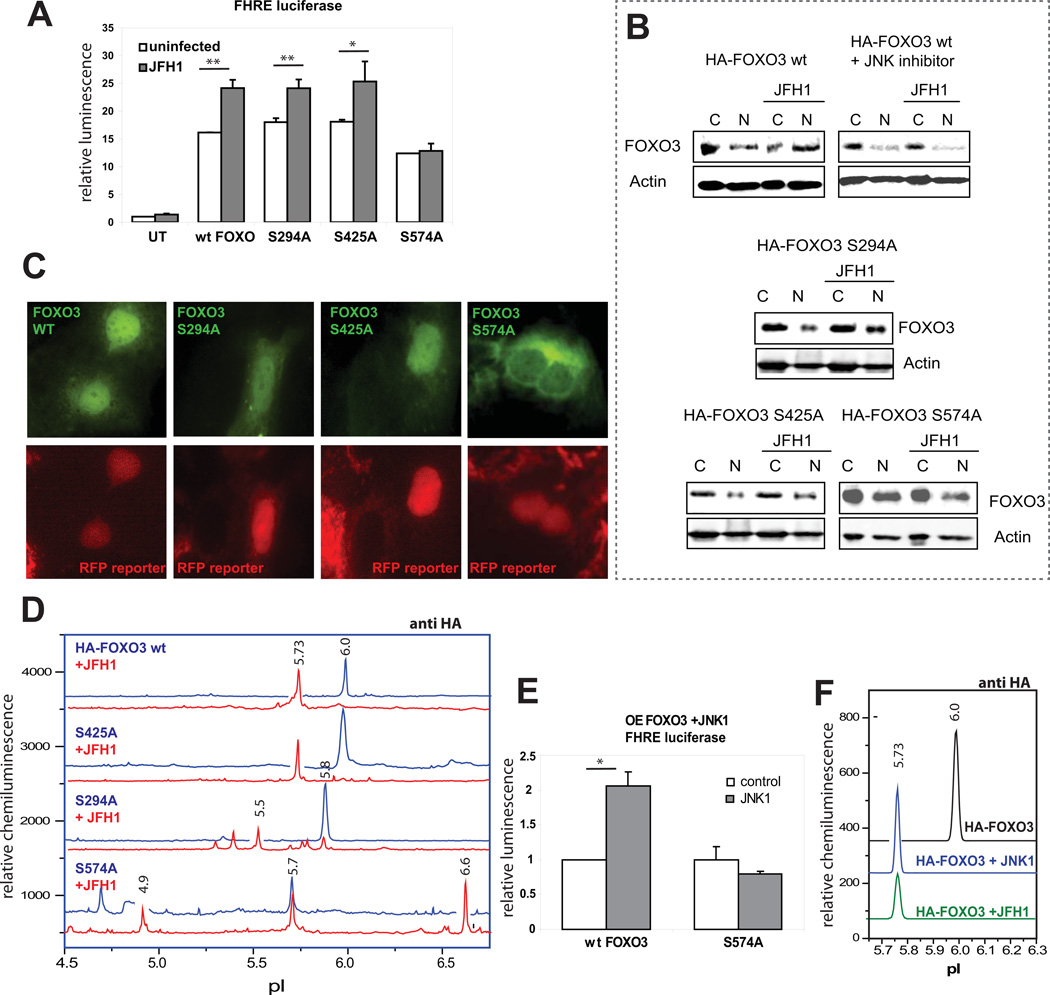
Figure 4. HCV induces JNK-mediated phosphorylation of FOXO3 at serine 574.
A. FHRE-luciferase reporter assays in control and HCV-infected Huh7.5 cells that were either untransfected (UT), or overexpressing HA-FOXO3 wt, S294A, S425A or S574A mutants of FOXO3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. B. Western blot analysis of overexpressed HA-FOXO3 wt, S294A, S425A and S574A in nuclear and cytosolic fractions of infected and control Huh7.5 cells. 20 µM JNK inhibitor (SP600125) was added as indicated. Numbers indicate the ratio of the density of the nuclear FOXO3 band in HCV infected/control cells. C. Immunofluorescence images of HCV-infected Huh7.5 reporter cells overexpressing HA-tagged wt or mutant FOXO3 constructs two days after infection. FOXO3 is in green (anti HA antibody), and RFP reporter protein is in red (infected cells have a nuclear distribution of the RFP reporter protein). D. cIEF analysis of nuclear FOXO3 species with anti-HA antibody in control and HCV-infected Huh7.5 cells overexpressing HA-tagged constructs of WT and mutant FOXO3. Baseline levels of each trace were shifted as for Fig. 1. E. FHRE-luciferase reporter assays in cells overexpressing WT or mutant FOXO3 S574A with or without co-transfection with Flag-MKK7-JNK1 fusion protein as indicated. F. cIEF analysis with anti-HA antibody of nuclear FOXO3 species in cells expressing wt HA-FOXO3 under control conditions, after cotransfection with the Flag-MKK7-JNK1 fusion protein, and after HCV infection.