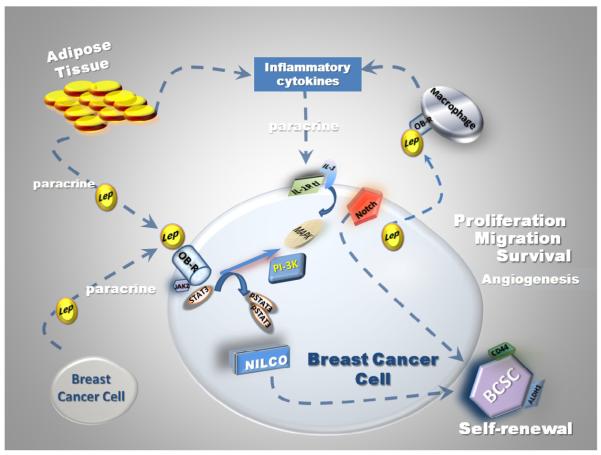
Fig. 1.
Role of leptin and inflammatory cytokine crosstalk in breast cancer. Progression of breast cancer is closely related to leptin and the actions of angiogenic and inflammatory cytokines. Breast cancer cells and associate stroma express an array of inflammatory cytokines in a simultaneous manner. Adipose tissue expresses tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin 6 (IL-6), which may cause obesity-related insulin resistance (Unkown, 2012; Kern et al., 2001). In primary breast cancer the expression of interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-6 and TNF-α correlated to tumor associate macrophages (TAM) and VEGF (Ueno et al., 2000). Leptin crosstalk to cytokines in breast cancer is closely related to tumor progression (proliferation, migration and metastasis), which also impact on self-renewal of breast cancer stem cells and tumor angiogenesis (Guo et al., 2012a).