Fig. 3.
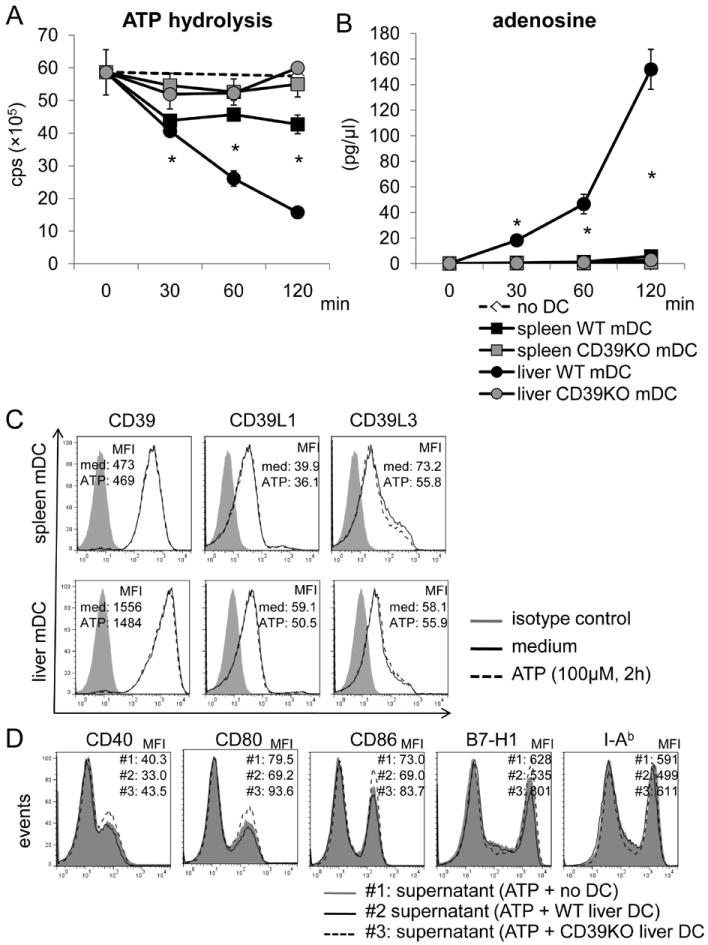
WT, but not CD39-/- B6 mouse liver mDC, hydrolyze ATP to a greater extent than WT spleen DC. WT or CD39-/- liver or spleen mDC (1×105) were cultured in ATP-containing medium (100nM) for the specified time. Supernatants were collected at each time point. (A) ATP concentration was determined by luminescence assay; cps=counts per second. (B) Adenosine concentration was measured by mass spectrometric analysis. n=3 experiments. *, p<0.05 comparing spleen and liver WT mDC. (C) Expression of CD39, CD39L1 and CD39L3 was determined by flow cytometry on liver and spleen mDC with or without ATP stimulation (100 μM) for 120 min. (D) WT or CD39-/- liver DC were cultured in ATP-containing medium for 3 hr. The cell-free culture medium was then transferred to WT liver mDC cultures that were stimulated with LPS for 18 hr. Liver mDC phenotype was determined by flow cytometry. Data in C and D are representative of 2 independent experiments.
