Fig. 4.
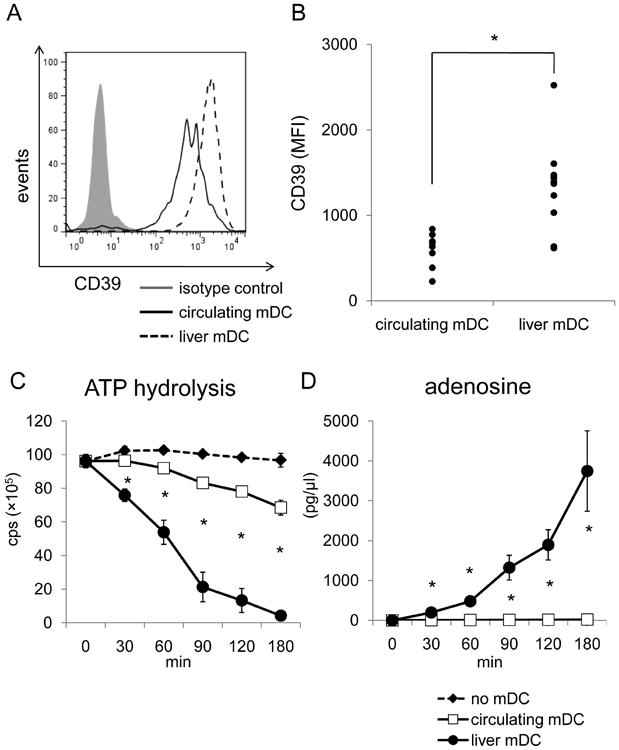
Freshly-isolated human liver mDC express higher levels of CD39 and hydrolyze ATP faster than circulating mDC. (A) The expression of CD39 by 7 individual human purified liver and peripheral blood mDC preparations was measured by flow cytometry, as described in the Materials and Methods. Liver and circulating mDC were defined by gating on CD45+, lineage (CD3, CD14, CD19, CD20)-, BDCA-1+cells. (B) Intensity (MFI) of CD39 expression was compared between human liver interstitial and blood-borne mDC. Each dot represents one individual (n=8 for circulating DC; n=10 for liver mDC). *, p<0.05. (C) Human liver mDC and circulating mDC were also purified using immunomagnetic beads and ATP hydrolysis assay conducted. (D) Adenosine concentrations were measured at each time point by mass spectrometric analysis. *, p<0.05 comparing circulating and liver mDC.
