Figure 3. Channelrhodopsin functions in vivo.
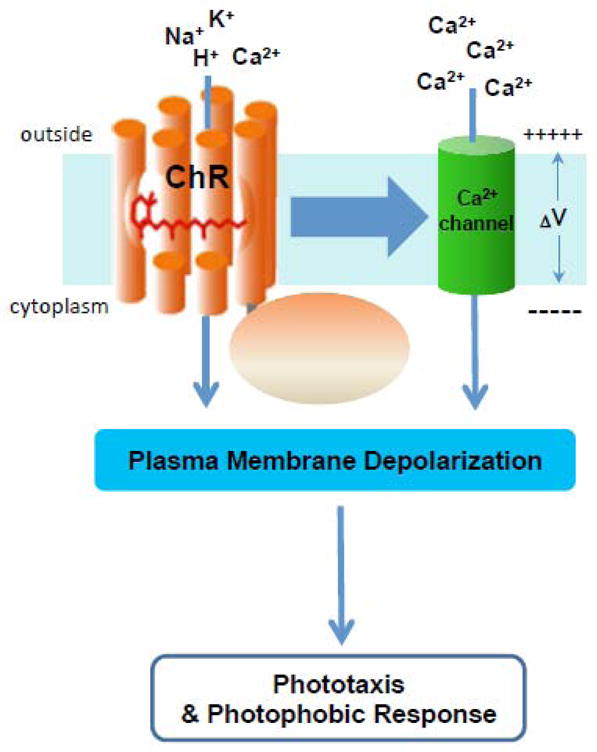
The figure depicts conclusions from studies of ChRfunction in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and related algae (reviewed in [77, 82–83]) that ChRs depolarize algal plasma membranes with two distinct mechanisms, a direct light-gated channel activity as depicted in Figure 1 attributable to the 7-helix domain, and an amplified current dependent on an unidentified Ca2+ channel activated by ChRs either by direct protein-protein interaction or through intermediare components.
