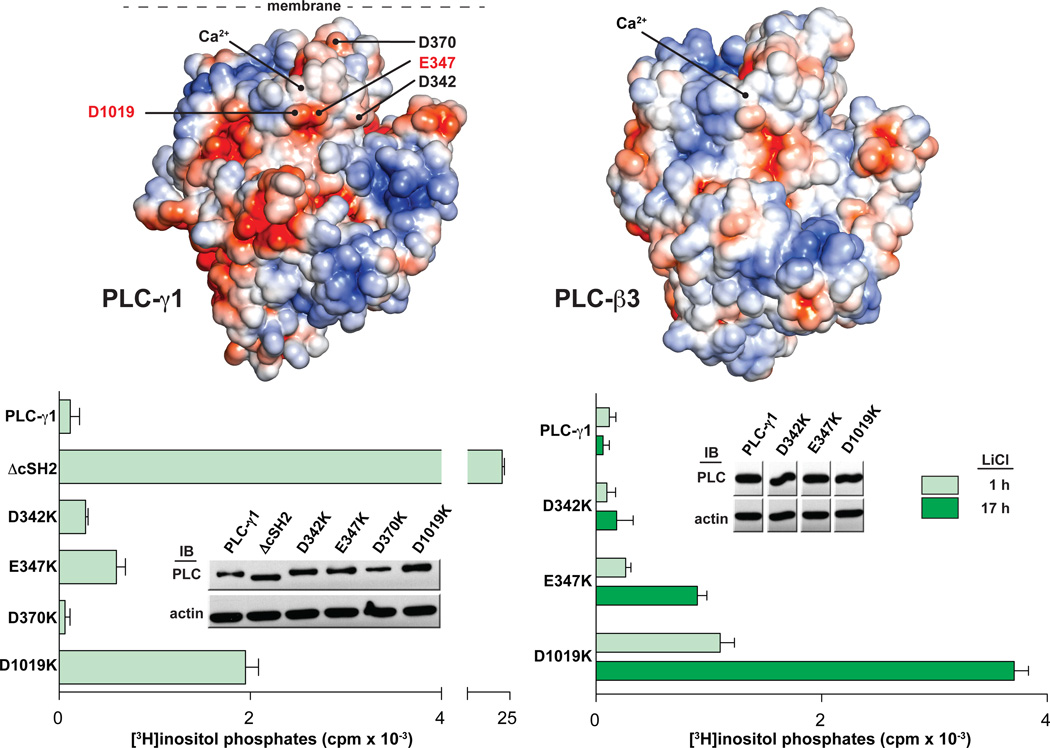
Fig. 4.
The catalytic core of PLC-γ1 contains a putative interface with the cSH2 domain. (A) The core of PLC-γ1 is electronegative. The solvent accessible surface of a homology model of PLC-γ1 lacking the X-Y linker (left) is colored according to electrostatic potential (red: −5 kT/e, blue: +5 kT/e). Residues selected for mutational analysis are labeled. The equivalent representation of PLC-β3 is shown at right. (B) Mutations near the active site of PLC-γ1 elevate basal activity. HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding either wild-type PLC-γ1 or PLC-γ1 harboring the indicated mutations in the TIM barrel. Accumulation of [3H]inositol phosphates was quantified after a one hour incubation with LiCl (left) or for the indicated times (right). The amount of radioactivity that accumulated in cells transfected with empty vector was subtracted from all measurements. Data are presented as the means ± S.E.M. of triplicate samples from a single experiment. Expression of PLC-γ1 constructs verified by western blots (insets).