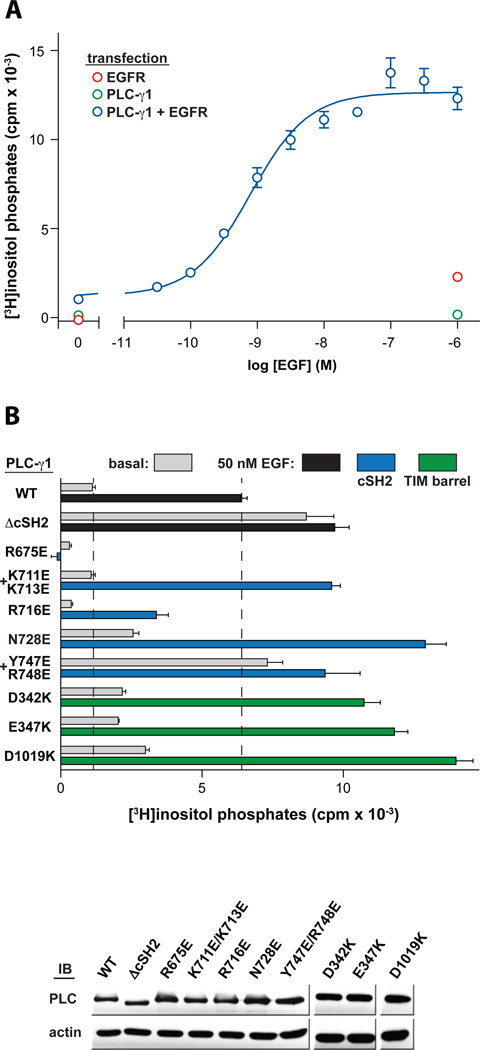
Fig. 5.
PLC-γ1 is activated to a similar extent by either EGFR-dependent phosphorylation or mutation of the BG loop. (A) Dose-dependent accumulation of inositol phosphates by EGF in cells overexpressing EGFR and PLC-γ1. HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding PLC-γ1, EGFR, or both constructs as indicated prior to challenge with EGF for 30 minutes and measurement of [3H]inositol phosphates. In each case, the level of radioactivity that accrued in cells not treated with LiCl was subtracted from all values. (B) Stimulation of PLC-γ1 by EGF is not further enhanced by mutation of the BG loop. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with plasmids encoding EGFR and either wild-type PLC-γ1 or the indicated mutant forms. Accumulation of [3H]inositol phosphates was quantified after a 30 minute challenge with vehicle (gray bars) or 50 nM EGF (black, blue, and green bars). The amount of radioactivity that accumulated in cells overexpressing EGFR following treatment with either vehicle or EGF was subtracted from each basal or EGF-treated condition, respectively. Activities of PLC-γ1 forms harboring mutations in either the cSH2 domain or the TIM barrel were measured independently and the results combined into a single graph for clarity. Expression of PLC-γ1 constructs verified by western blots of cell lysates (bottom). Data are presented as the means ± S.E.M. of triplicate samples from single experiments and are representative of three independent experiments in panel B.