Fig 4.
Functional analysis of Csd6 enzymatic activity and expression levels.
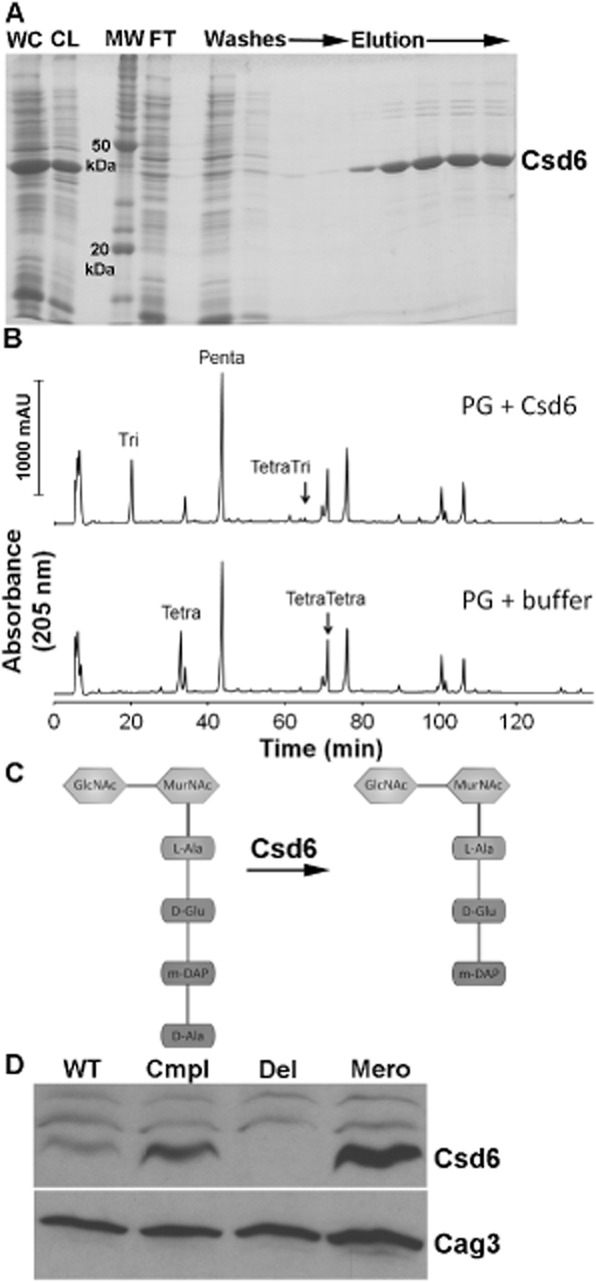
A. SDS-PAGE gel depicting steps in the purification of oligohistidine-tagged H. pylori Csd6 protein from E. coli cells. The protein was purified using Ni-NTA resin as described in Experimental procedures. WC, induced whole-cell lysate; CL, cleared lysate; MW, molecular weight markers; FT, flow-through.
B. HPLC analysis of muropeptides released from purified peptidoglycan (PG, obtained from the Δcsd1csd6 mutant, strain DBH11) upon treatment with His-Csd6 or buffer followed by cellosyl digestion. Loss of monomeric tetrapeptides with formation of monomeric tripeptides in the presence of Csd6 is indicative of the protein having ld-carboxypeptidase activity.
C. Schematic of the predicted activity of Csd6 based on experiment in (C) showing the substrate (tetrapeptide) and product (tripeptide).
D. Antibody-based detection of Csd6 in whole-cell extracts prepared at equal cell density. Blots were stripped and re-probed with antisera against another periplasmic protein, Cag3, for quantitative expression analyses. One of three representative experiments is shown. WT, wild-type (LSH100); Cmpl, csd6 complement (TSH31); Del, csd6 null allele (TSH17), Mero, csd6 merodiploid (TSH35).
