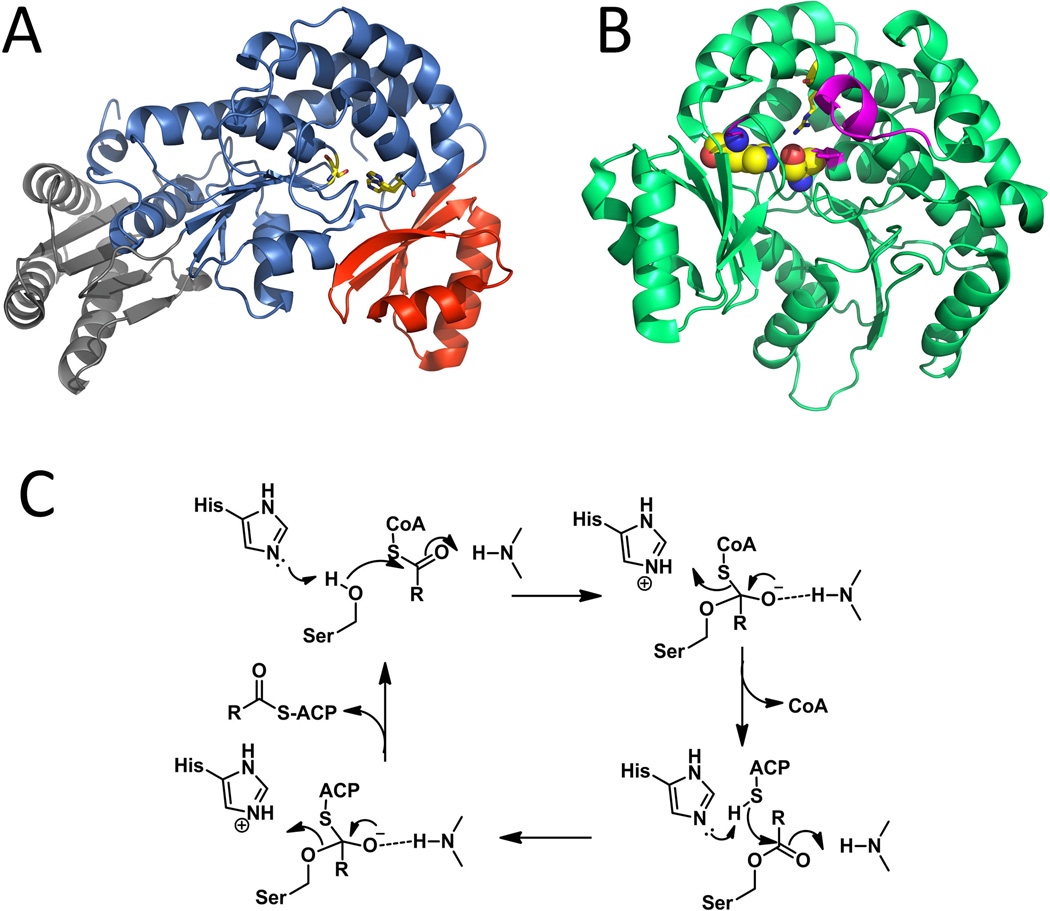
Figure 8.
Selected AT structures and typical catalytic mechanism. (A) Structure of ATDYN10 from dynemicin pathway. KS-AT linker (gray), α/β hydrolases-like core (Blue) and ferrodoxin-like smaller subdomain (Red). The catalytic His-Ser dyad is shown as sticks. PDB code: 4AMP. (B) Residues and region important to substrate binding or selection in DEBS AT5: catalytic dyad are shown as spheres; the arginine stabilizes the substrate 3-carboxylate group is shown as sticks; important region that defines the substrate specificity are labeled in magentas. PDB code: 2HG4. (C) catalytic mechanism of AT. 215×188mm (300 × 300 DPI).