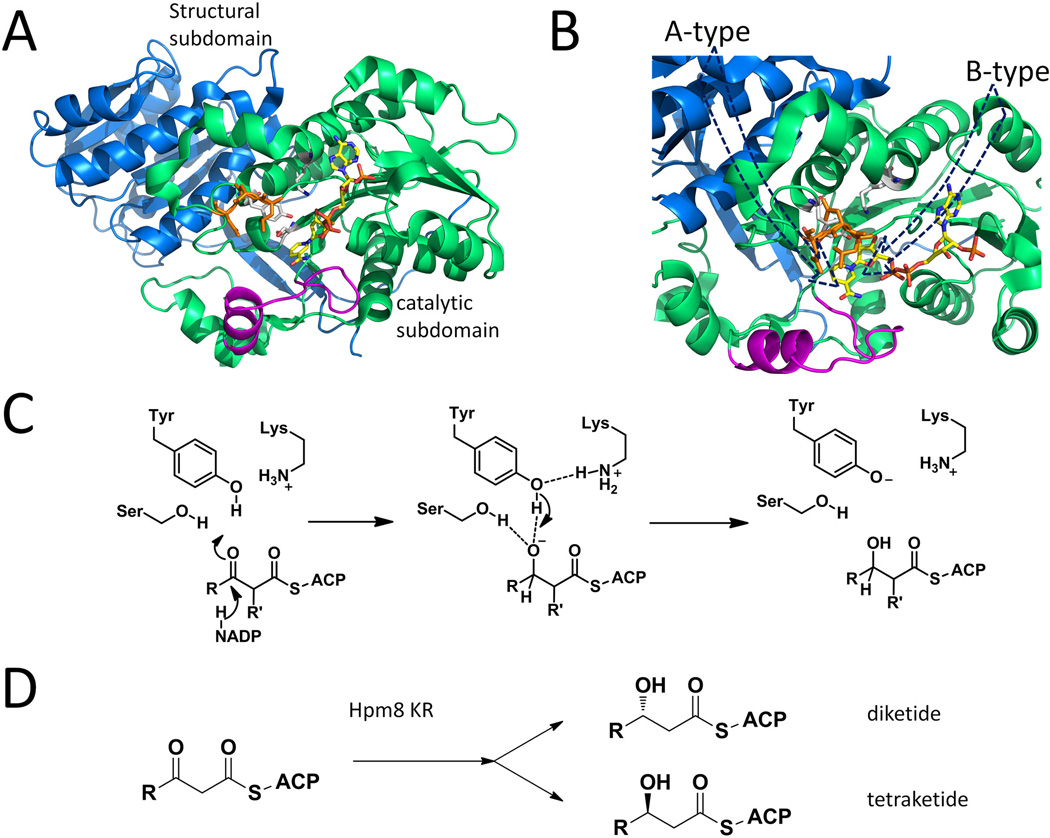
Figure 9.
Selected KR structures and typical catalytic mechanism. (A) DEBS KR1 with cofactor binding, catalytic triads are shown as sticks. Blue: structural subdomain; Green: catalytic subdomain; Orange: “LDD” moiety shown as sticks. Magenta: Lid helix and loop. PDB code: 2FR0. (B) Different paths of entrance result in the different product stereochemistries in A and B type KRs. The presence of orange DLL loop in B-type KR will prevent substrate from entering behind the magenta lid. (C) Mechanism of KR catalyzed reduction. (D) Substrate-tuned stereoselectivity in Hpm8KR. 215×176mm (300 × 300 DPI).