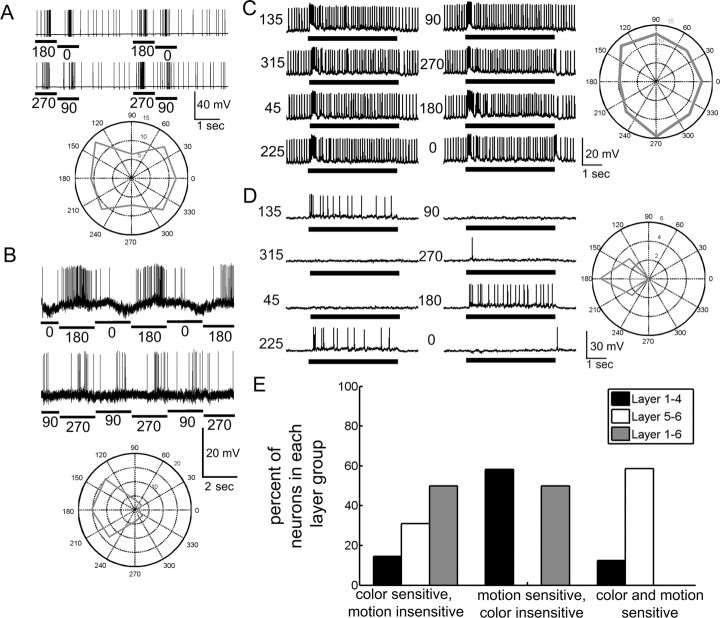
Figure 6.
Motion response types. A–D, In these examples, the neurons were presented a large moving bar (A, B) or a wide-field moving grating (C, D). The spike rates significantly changed in response to the motion cues presented. To examine the directionality, we plotted the spike rates for each direction on a polar plot for each stimulus. B, D, We found clear directionality sensitivities for some neurons. A, C, Other neurons did not exhibit clear directionality preferences. In all cases, black bars signify the duration of the motion cue. Numbers signify the direction of movement in degress relative to the eye. E, When we compared the response properties of neurons where color and motion cues were tested among the layers, we found different percentages of neurons which were sensitive to color, to motion, or to both. Notably, the layer 5–6 neurons were color and motion sensitive, whereas most of the layer 1–4 neurons were motion sensitive but color insensitive. The remaining tested neurons had no motion responses and were broadly sensitive to the different colors.