Table 2.
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
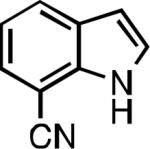
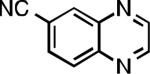
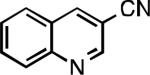
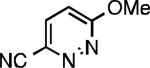
| L1 95% (0.7% P1) | L2 97% (1% P2) | L2 93% (2% P2) | L2 64% (4% P2)[c] |
|
|
|
|
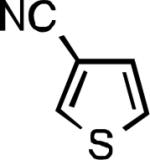
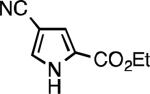
| L2 66% (1.6% P2)[d] | L2 91% (4% P2) | L2 91% (4% P2) | L2 92% (1.4% P2) |
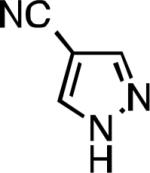
|
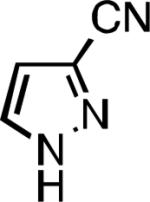
|
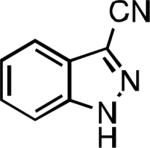
|
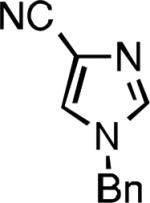
|
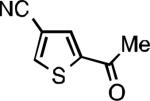
| L2 93% (1% P2) | L3 64% (5% P3)[e] | L2 94% (4% P2) | L3 99% (1.5% P3) |
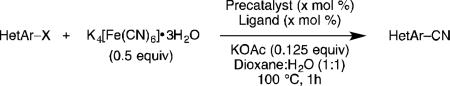
Reaction conditions: aryl chloride (1 mmol), K4[Fe(CN)6]•3H2O (0.5 equiv), precatalyst (× mol %), ligand (× mol %) KOAc (0.125 equiv), dioxane (2.5 mL), H2O (2.5 mL).
Isolated yields, average of 2 independent runs.
0.5 equiv KOAc.
Low yield due to product volatility.
Isolated as HCl salt, 95:5 mixture of HetArCN:HetArBr.
