Fig. 2.
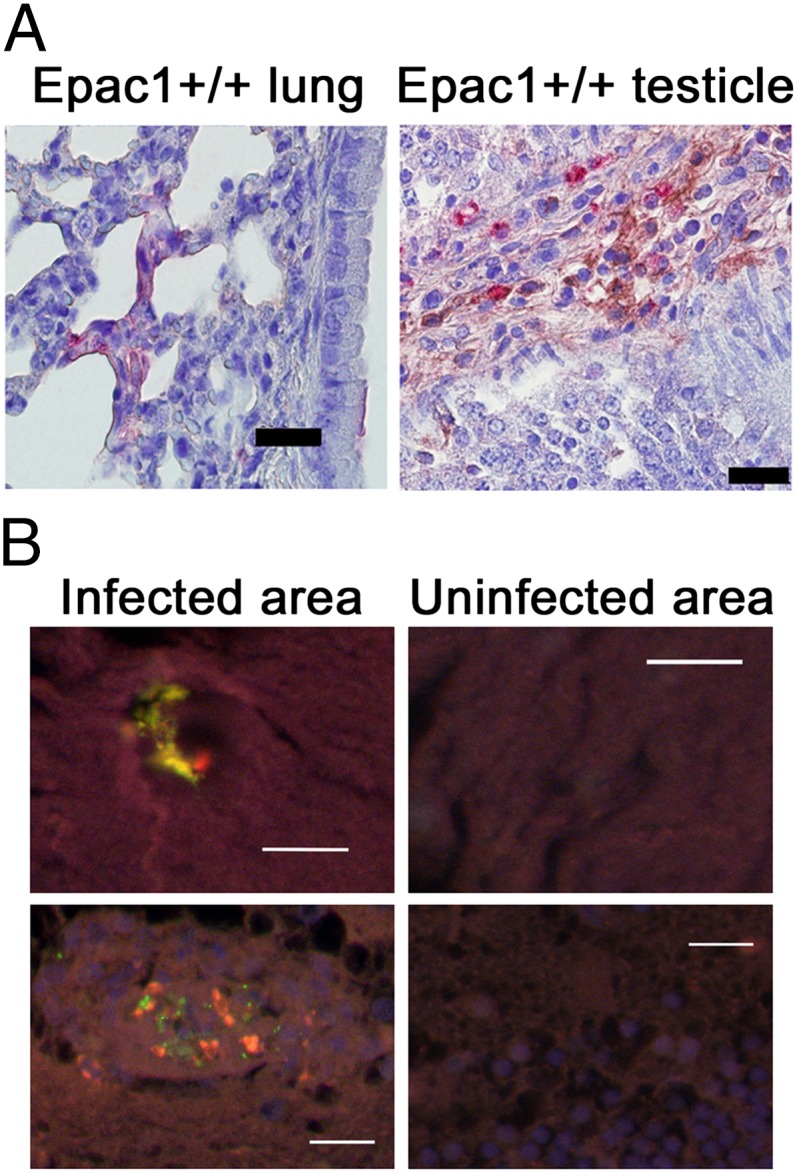
Rickettsial infection induces increased expression of Epac1 in rickettsial lesions. (A) Representative dual-target IHC staining of rickettsiae (red) and Epac1 (brown) in lung and testis from Epac1+/+ mice (n = 12). Rickettsiae and Epac1 were stained using alkaline phosphatase–fast red and peroxidase–DAB, respectively. Nuclei of mouse cells were counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). (B) Representative dual-target IF staining of rickettsiae (green) and Epac1 (red) in brain from an archived pediatric case of fatal RMSF. Nuclei of human cells are counterstained with DAPI (blue). (Scale bars: 20 µm.)
