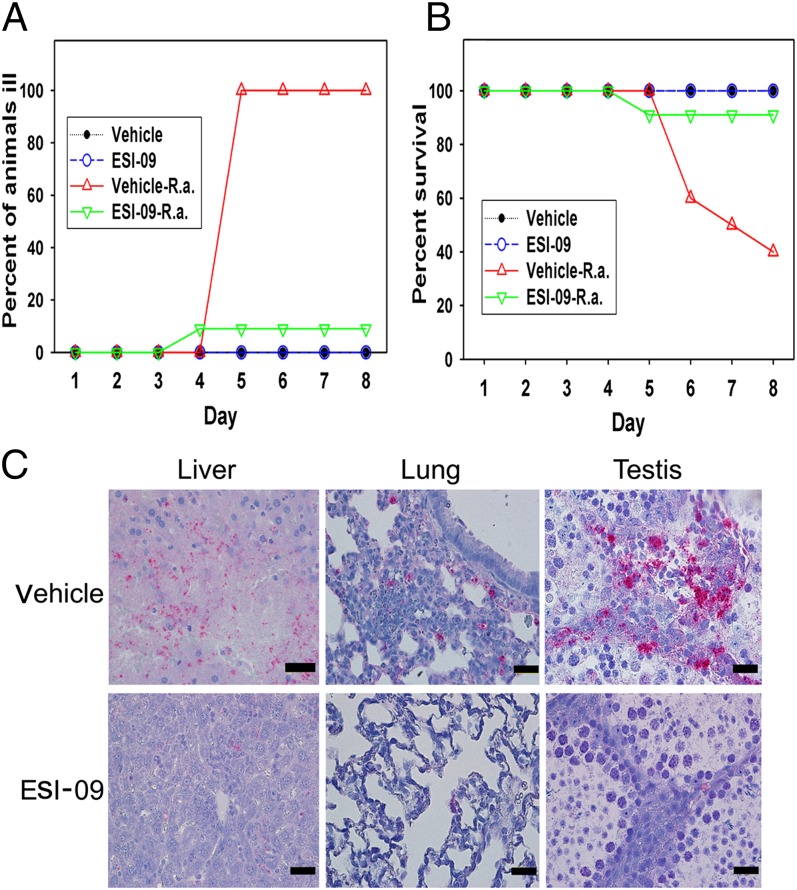
Fig. 5.
Pharmacological inhibition of Epac1 protects WT mice against rickettsial infection. Disease progression (A) and survival (B) of ESI-09–treated (n = 11) and vehicle-treated (n = 10) Epac1+/+ (WT) mice were monitored daily for 8 d postinfection with R. australis or mock infection. (C) Representative IHC staining of SFG rickettsiae (red) in liver, lung, and testis from ESI-09– and vehicle-treated Epac1+/+ (WT) mice. Rickettsiae were stained using alkaline phosphatase–fast red, whereas nuclei of mouse cells were counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). (Scale bars: 20 µm.)