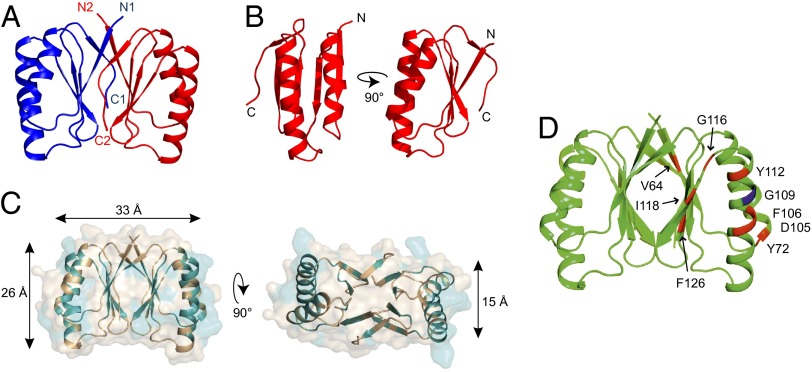
Fig. 3.
Crystal structure of B. subtilis SepF residues 61–140. (A) The crystal structure reveals a dimer whereby the C-terminal β-strand of one monomer (C1, C2) joins the β-sheet of the other monomer and is parallel to its N-terminal β-strand (N1, N2). Structure statistics are listed in Table S1. (B) Monomer of SepF C-terminal domain. (C) Conserved residues are highlighted in teal on the SepF dimer structure. Most conserved residues are located at the interface between monomers (β-sheets) and the interface between dimers (α-helices). Dimensions indicated by arrows are based on the protein backbone. (D) FtsZ-interaction mutants from the yeast two-hybrid screen are indicated on the crystal structure. G109 residue is indicated in blue.