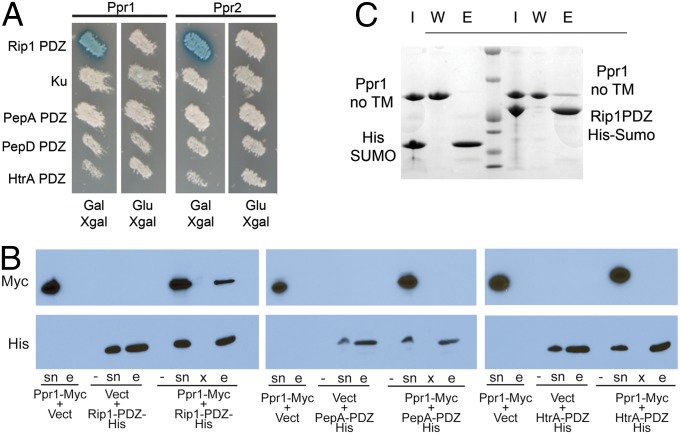
Fig. 2.
Ppr1 is a specific interactor of the Rip1-PDZ domain. (A) EGY48 yeast cells containing plasmids encoding AD fusions to Ppr1 (encoded by M. tuberculosis Rv3333c) or Ppr2 (encoded by M. tuberculosis Rv3439c) and a LexA-LacZ reporter plasmid were tested with LexA-DNA BD fusions to Rip1-PDZ, the NHEJ protein Ku, PepA-PDZ, PepD-PDZ, or HtrA-PDZ. The Ppr1 and Ppr2 AD fusions are under the control of a galactose-inducible promoter, which is repressed by glucose. (B) Specificity of the Ppr1-Rip1-PDZ interaction. Ppr1-Myc was coexpressed in E. coli with either Rip1-PDZ-His, PepA-PDZ-His, or HtrA-PDZ-His. Soluble lysates from the indicated combinations of expressed proteins or vector controls were subjected to metal-affinity chromatography to purify histidine tagged proteins. Supernatants (sn) and eluted proteins (e) were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Myc or anti-His antibodies. The lanes labeled “-” are no-isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) control samples, and the lanes labeled “x” are blank lanes. (C) Ppr1 and Rip1-PDZ interact in vitro. Ppr1 lacking its transmembrane domain (Ppr1-no TM; amino acids 32–281) and either His-SUMO or His-SUMO-Rip1-PDZ were mixed and purified by metal-affinity chromatography. Bound proteins were eluted with imidazole, and the input protein (I), wash (W), and elution (E) were separated by SDS/PAGE and proteins visualized by staining with Coomassie blue.