Fig. 5.
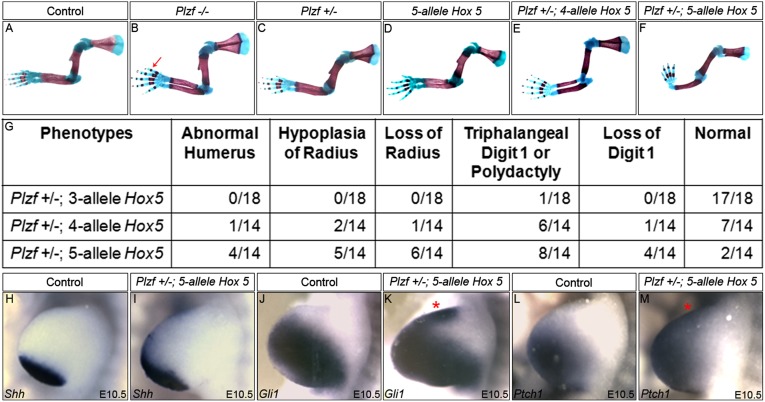
Hox5 and Plzf genetically interact to pattern the anterior limb and Shh expression in vivo. (A–G) Skeletal preparations from E18.5 Plzf, 5-allele Hox5, and compound Hox5;Plzf mutants. Plzf heterozygotes and embryos with up to five mutant Hox5 alleles (Hox5Aabbcc) are indistinguishable from controls (C and D), whereas Plzf mutants exhibit preaxial defects with 100% penetrance in our background (B; arrow denotes triphalangeal digit 1). Compound mutants heterozygous for Plzf plus three mutant Hox5 alleles rarely display a phenotype (G), but Plzf heterozygotes with four or five mutant Hox5 alleles display increases in the penetrance of anterior limb defects (E–G), demonstrating strong genetic interaction between Hox5 and Plzf. (H–M) The Shh pathway is derepressed in Hox5;Plzf compound mutants. Shh (H and I), Gli1 (J and K), and Ptch1 (L and M) are ectopically expressed in Plzf +/−;Hox5 5-allele compound mutants compared with controls. Controls include WT, Plzf heterozygous, and compound Hox5 mutants with five or fewer mutant alleles; red asterisks denote anteriorized expression.