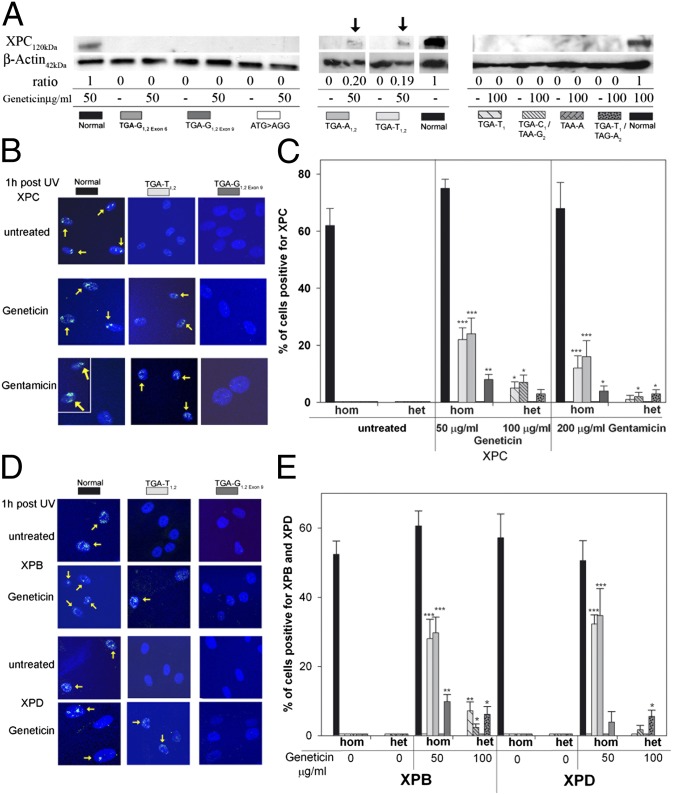
Fig. 2.
Effect of Geneticin and gentamicin on XPC, XPB, and XPD proteins. (A) XP-C cells were incubated with geneticin for 4 d and immunoblot was performed. XPC protein was detectable via immunoblotting in Geneticin-treated TGA-T1,2 and TGA-A1,2 only (arrows). The ratio (%) of the intensity of the XPC band to b-actin band is indicated. In total, three different experiments were performed. Shown are three representative western blots. (B) Cells were incubated with Geneticin or gentamicin for 3 d, and an immunofluorescence assay 1 h after local UV irradiation was performed. Geneticin and gentamicin induce post-UV XPC protein localization in TGA-T1,2 (yellow arrows) but not in TGA-G1,2exon 6. For the gentamicin-treated normal cells (Lower Left), two representative areas of the same coverslip are shown. (C) Quantification of XPC protein detected via immunofluorescence at sites of UV damage 1 h after UV exposure. One hundred nuclei were scored. Bars indicate mean ± SD of the percent positive cells for XPC. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005. (D) Cells were incubated with Geneticin for 3 d, and an immunofluorescence assay 1 h after local UV irradiation was performed. Geneticin induced post-UV XPB or XPD protein recruitment in TGA-T1,2 (yellow arrows) but not in TGA-G1,2exon 6. (E) Quantification of XPB and XPD proteins detected via immunfluorescence at sites of UV damage 1 h after UV exposure. Bars indicate mean ± SD of the percent positive cells for XPB and XPD, and 100 nuclei were scored. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005.