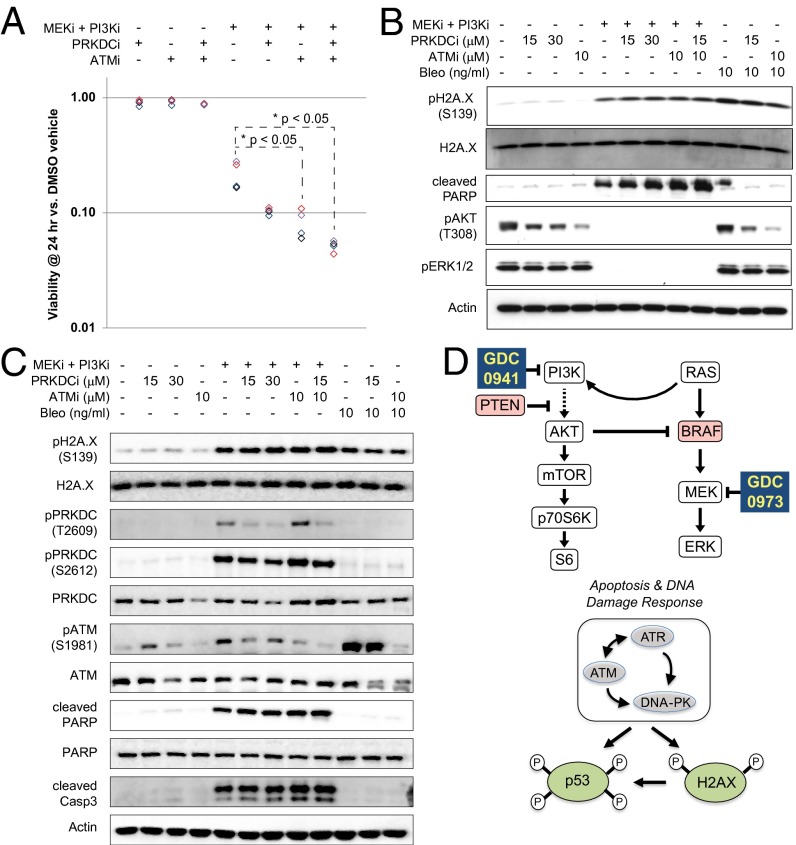
Fig. 4.
Coinhibition of ATM and PRKDC enhances cell killing by GDC-0973 and GDC-0941. (A) Luminescent-based viability assays performed on A2058 cells pretreated for 90 min with DMSO, 15 μM NU7026 (PRKDCi), 10 μM KU55933 (ATMi), or 15 μM NU7026 + 10 μM KU55933. Cells subsequently were treated for 24 h with either DMSO or GDC-0973+GDC-0941 (MEKi + PI3Ki; 2.5 μM each). Average values (n = 6 technical replicates) are reported relative to DMSO for n = 4 replicate experiments. *P < 0.05 determined by paired student's t test followed by Bonferroni correction. (B) Blots of A2058 lysates treated for 3 h with DMSO, MEKi + PI3Ki (2.5 μM each), 15–30 μM PRKDCi, and/or 10 μM ATMi, as indicated. As a control for DDR, cells also were treated with bleomycin (10 ng/mL). Blots were probed against H2AX pSer139, cleaved PARP, AKT pThr308, and ERK1/2 pThr202/Tyr204, with total H2AX and actin as controls. (C) Blots of A2058 lysates treated as in B and probed for PRKDC pThr2609, PRKDC pSer2609, ATM pSer1981, and cleaved caspase 3, with total H2AX, PRKDC, ATM, PARP, and actin serving as controls. (D) Diagram depicting the mechanism of action for GDC-0973 and GDC-0941in melanoma cells. MAPK and PI3K pathways are drivers of cell proliferation and survival, here through the loss of PTEN tumor-suppressor activity and/or oncogenic activation of BRAF (red). Mutational activation of RAS, PI3K, and/or AKT also can signal through these pathways. Dual inhibition of the MEK/PI3K pathways decreases cell-survival signaling leading to apoptosis, activation of DNA damage-response kinases (DNA-PK, ATM, and ATR), and phosphorylation of downstream biomarkers H2AX and p53.