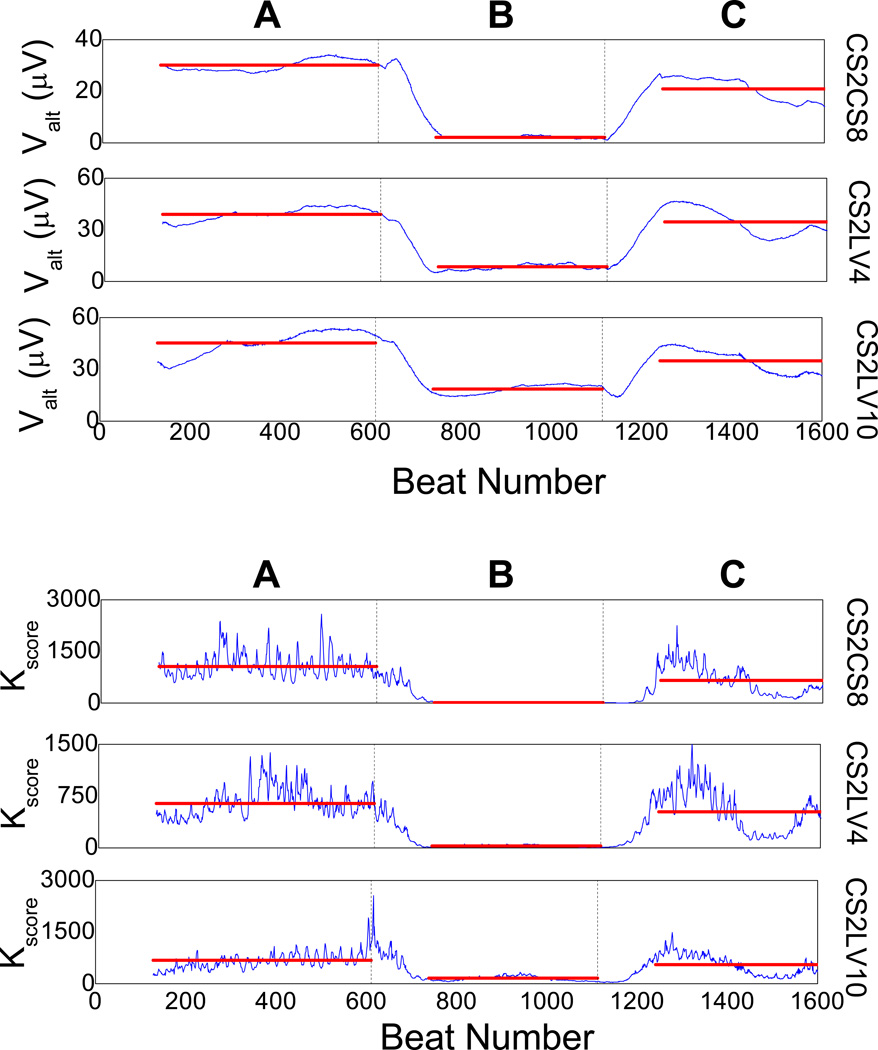
Figure 6.
Utility of the T-wave alternans (TWA) phase to suppress spontaneously occurring alternans in sinus rhythm during acute myocardial ischemia. Alternans voltage and Kscore are plotted for the intra-cardiac lead configuration CS2CS8, CS2LV4 and CS2LV10. In-phase suppression pacing intervention is delivered from the right ventricle apex (RV12; amplitude: +4 mA, width: 10 msec, coupling to R-wave: 10 msec). A: spontaneously occurring alternans is visible at baseline, B: R-wave triggered pacing is delivered from RV12 on every even beat with a positive polarity pulse, which results to significant reduction of TWA (77.59% reduction of the alternans voltage compared to baseline, p<0.0001; 92.55% reduction of the Kscore compared to baseline, p<0.0001), C: R-wave triggered pacing is discontinued and both alternans voltage and Kscore increase to the baseline level during sinus rhythm. Transitions A to C occur correspondingly at times marked by solid vertical black lines, while the colored horizontal lines during each intervention indicate the mean value of the alternans voltage and Kscore during that intervention.