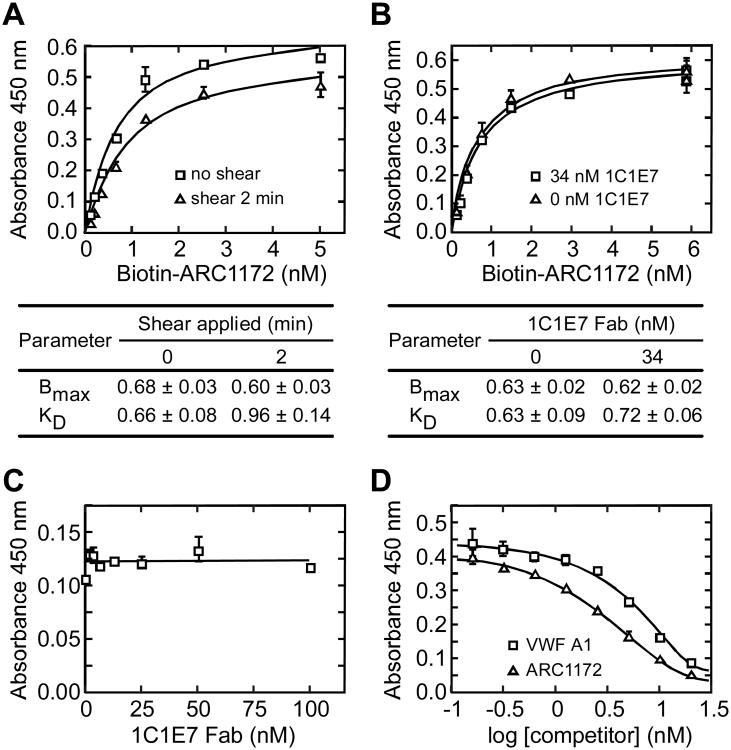
Figure 6. Analysis of VWF A1-ARC1172 binding.
Microtiter plates were coated with rabbit anti-VWF (A,B,C) or monoclonal anti-VWF CK 62-12 (D) as described under “Experimental Procedures”. Error bars represent SE. (A) Shear stress does not affect ARC1172-VWF binding. VWF (5 μg/mL) and biotin-ARC1172 (5, 2.5, 1.25, 0.625, 0.3125, 0.155, 0.0775 nM) were mixed and treated without (squares) or with (triangles) shear stress for 2 min (Zhang et al., 2007) before assessment of binding. Values ± SD for maximal binding (Bmax) and KD are tabulated. (B) Binding of biotin-ARC1172 (2.5 nM) to VWF (5 μg/mL) was similar without (triangles) or with (squares) monoclonal antibody 1C1E7 Fab (34 nM), which binds VWF domain D3 and enhances VWF binding to GPIbα with an EC50 of ∼40 nM (Ulrichts et al., 2006). Values ± SD for Bmax and KD are tabulated. (C) 1C1E7 Fab did not inhibit biotin-ARC1172 (2 nM) binding to VWF (0.5 μg/mL). (D) Recombinant VWF A1 (squares) or unbiotinylated ARC1172 (triangles) inhibited the binding of biotin-ARC1172 (1 nM) to VWF (5 μg/mL).