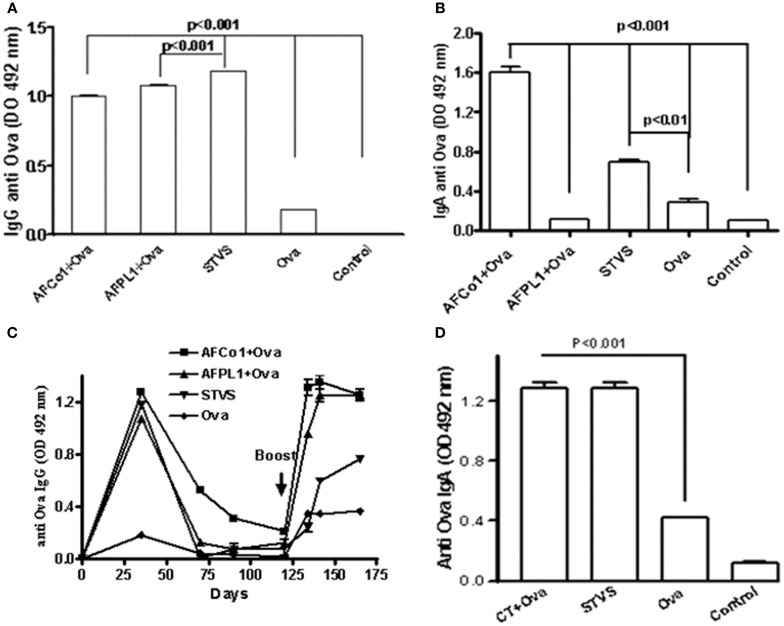
Figure 6.
Specific anti-Ova immune response induced by single-time vaccination strategy (SinTimVaS). BALB/c mice were immunized with: three i.n. doses (0, 7, 14 days) of AFCo1 + Ova (50 μg/25 μg in 25 μL per animal, 12.5 μL through each nostril); two i.m. doses (0, 14 days) of AFPL1 + Ova (12.5 μg/10 μg in 50 μL per animal); both treatments at the same time in SinTimVaS and Ova as the control. Other groups were followed until specific IgG decreased and a booster Ova dose at day 125 was administered. Other groups using cholera toxin (CT) as the adjuvant instead of AFCo1/AFPL1 were also evaluated. These were administered via the nasal route CT + Ova (5 μg/50 μg in 25 μL per animal, 12.5 μL through each nostril) and simultaneously one intramuscular dose of CT + Ova (5 μg/20 μg in 50 μL) was administered. For anti-Ova IgG or IgA, serum samples at 21 days after the last dose were used. The determination was carried out by ELISA. Data were expressed as averages and standard deviation of OD of two determinations in three independent experiments. Specific Ova IgG (A); (B,D) specific Ova IgA; and (C) specific Ova IgG after a booster Ova dose. Significant differences between the means of different groups were determined by a Tukey multiple comparison test using Graph Pad Prism 4 software (Calif.). A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.