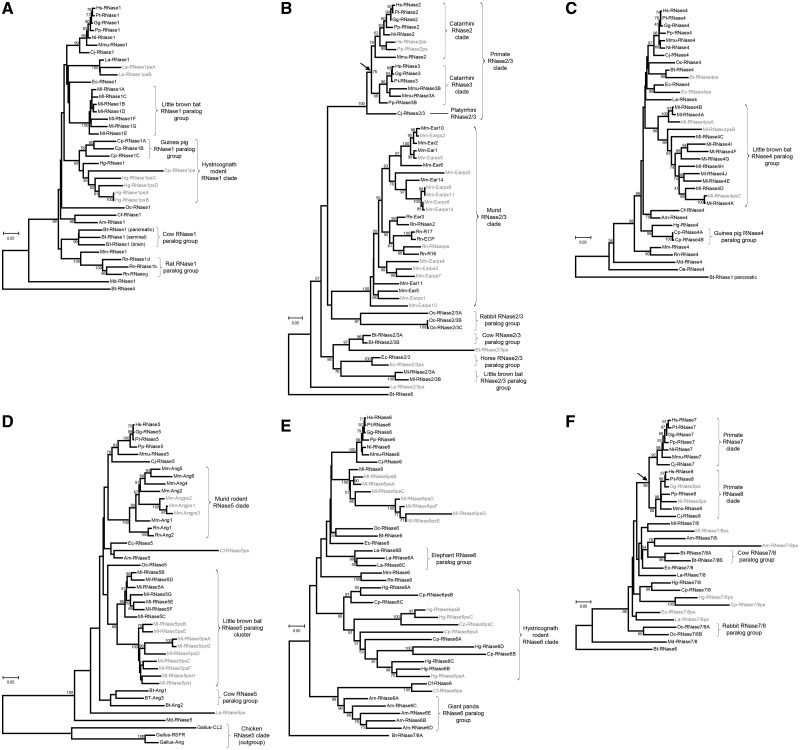
Fig. 4.—
Phylogenetic trees of functional genes and pseudogenes of the six canonical RNase gene lineages. For all trees, the neighbor-joining method with Kimura’s two-parameter, the complete-deletion option, and 1,000 bootstrap replications were used. Trees for RNase1 (A), RNase2/3 (B), RNase4 (C), RNase5 (D), RNase6 (E), and RNase7/8 (F) were made with 454, 475, 471, 439, 501, and 483 nucleotide sites, respectively. Pseudogenes are distinguished with gray color. Paralog groups are marked with brackets. Arrows in (B) and (F) indicate the time of duplication of RNase2 and RNase3 (B) and that of RNase7 and RNase8 (F), respectively. The scale bar number indicates the number of nucleotide substitutions per site.