Fig. 1.—
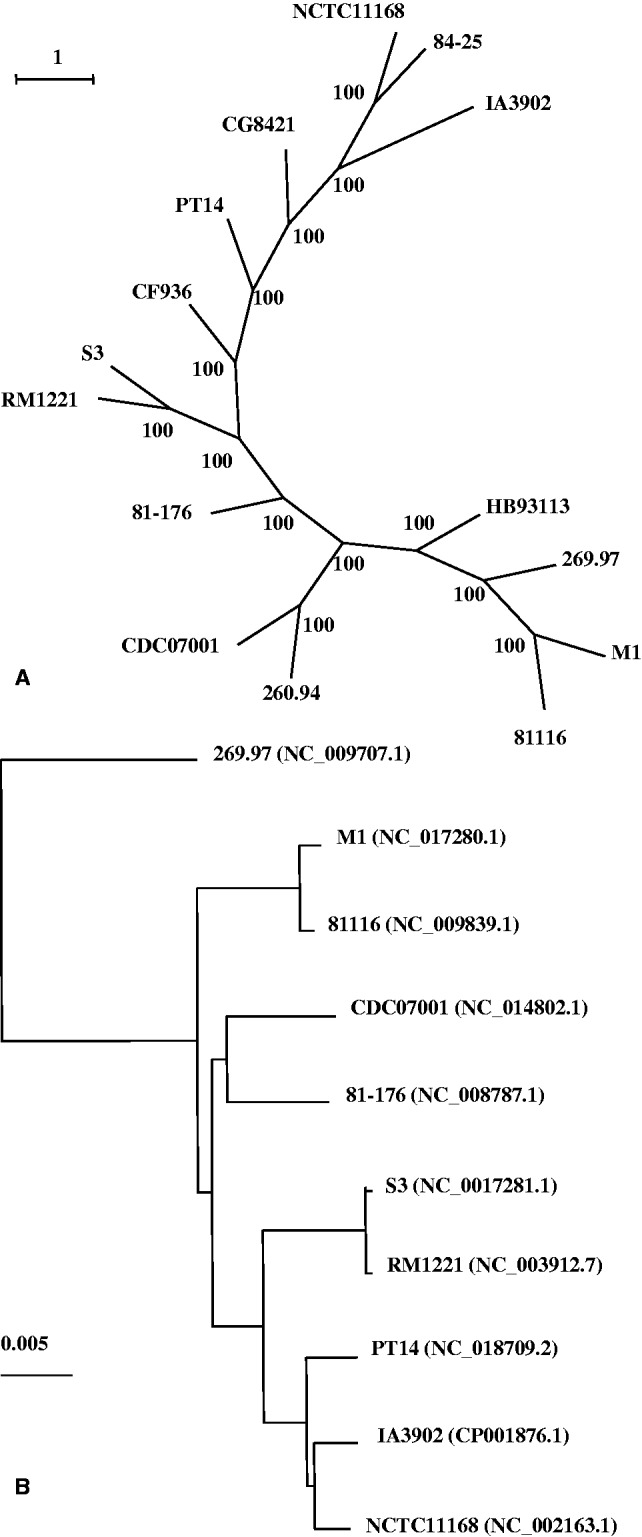
Phylogenetic analysis of Campylobacter jejuni IA3902 and other genome-sequenced strains. (A) The maximum-likelihood protein tree for genome-sequenced C. jejuni strains were generated from concatenated multiple alignments of 12 conserved proteins (InfB, FusA, Tuf, RplB, RpsE, RpsH, RpsK,TopA, Ffh, GyrB, LepA, and PyrG). The numbers along the branches of the tree denote percent occurrence of nodes among 100 bootstrap replicates. The scale bar represents the number of amino acid substitutions per site. (B) A dendrogram generated from whole genomic Blast shows the genetic relationship of C. jejuni strains, for which whole-genome sequences are available in GenBank. Genome accession numbers are shown in the parentheses. The scale bar represents the number of nucleotide substitutions per site.
