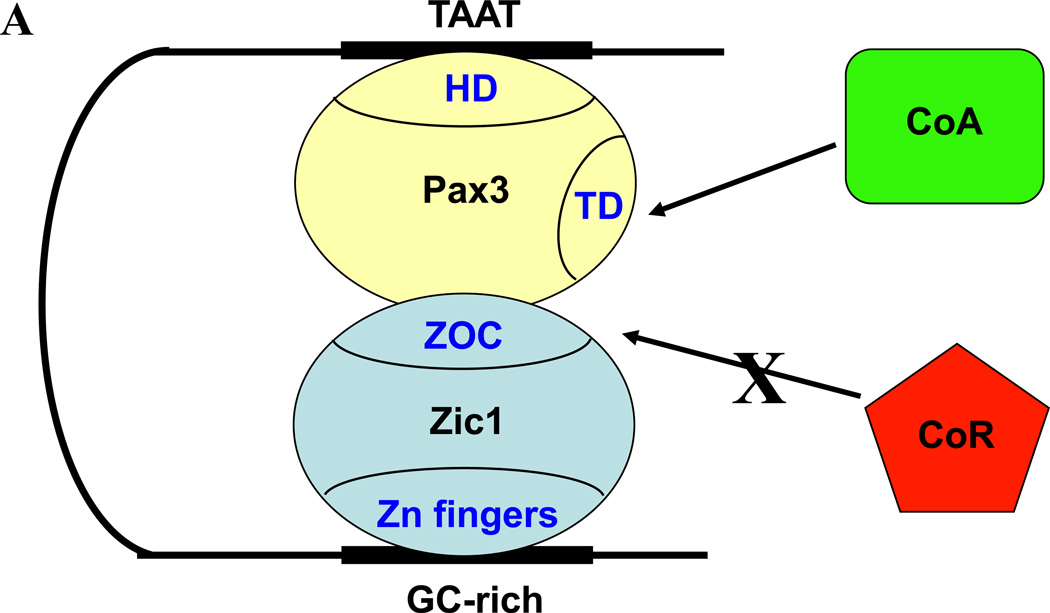
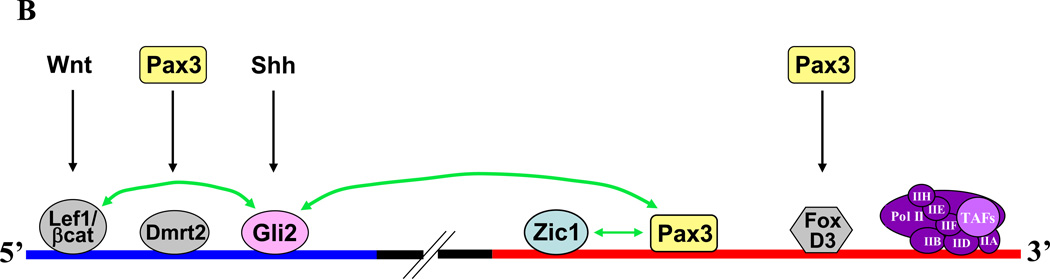
Fig. 5. Cooperation among several distinct pathways promotes myogenesis in the epaxial somite.
A. Model of Pax3-Zic1 synergy. Pax3 binds the homeodomain motif in the Myf5 promoter (TAAT) via its homeodomain (HD), and Zic1 binds GC-rich sequences via its zinc finger domain. Interaction between Pax3 and the ZOC domain of Zic1 prevents the latter from recruiting transcriptional co-repressors (CoR). The transactivation domain (TD) of Pax3 recruits transcriptional co-activators (CoA). B. Transcription factors and upstream signaling pathways regulating Myf5 expression in the epaxial somite. The blue bar indicates the Myf5 ES enhancer, and the red bar indicates the Myf5 promoter. Green arrows indicate synergistic interactions between transcription factors. Shh signaling is required for Gli activation of the ES enhancer via a single essential motif (21, 56). Wnt and Shh signaling culminate in synergy between LEF1/β-catenin bound to three motifs (shown as a single motif for simplicity) in the ES enhancer and Gli bound downstream (5). Pax3 activates Myf5 in the epaxial somite indirectly, by driving expression of the Dmrt2 transcription factor, which activates the ES enhancer (51), and in zebrafish, by driving expression of FoxD3, which activates the Myf5 promoter (32). In the current work, Pax3 also activates epaxial Myf5 expression directly, by binding a homeodomain motif in the Myf5 promoter and synergizing with both Gli2, bound to the ES enhancer, and Zic1, which recognizes GC-rich motifs in the promoter. Refer to the text for more details.