Abstract
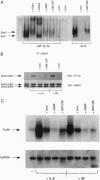
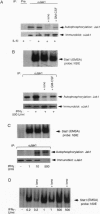
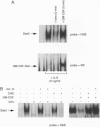
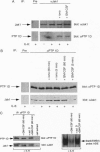
An important component of cytokine regulation of cell growth and differentiation is rapid transcriptional activation of genes by the JAK-STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) signaling pathway. Ligation of cytokine receptors results in tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of receptor-associated Jak protein tyrosine kinases and cytoplasmic STAT transcription factors, which then translocate to the nucleus. We describe the interruption of cytokine triggered JAK-STAT signals by cAMP, the calcium ionophore ionomycin, and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Jak1 kinase activity, interleukin 6-induced gene activation, Stat3 tyrosine phosphorylation, and DNA-binding were inhibited, as was activation of Jak1 and Stat1 by interferon gamma. The kinetics and requirement for new RNA and protein synthesis for inhibition of interleukin 6 by ionomycin and GM-CSF differed, but both agents increased the association of Jak1 with protein tyrosine phosphatase ID (SH2-containing phosphatase 2). Our results demonstrate that crosstalk with distinct signaling pathways can inhibit JAK-STAT signal transduction, and suggest approaches for modulating cytokine activity during immune responses and inflammatory processes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Nishio Y., Inoue M., Wang X. J., Wei S., Matsusaka T., Yoshida K., Sudo T., Naruto M., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azam M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Kreider B. L., Xia M., Quelle F., Basu R., Saris C., Tempst P., Ihle J. N., Schindler C. Interleukin-3 signals through multiple isoforms of Stat5. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 3;14(7):1402–1411. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach E. A., Szabo S. J., Dighe A. S., Ashkenazi A., Aguet M., Murphy K. M., Schreiber R. D. Ligand-induced autoregulation of IFN-gamma receptor beta chain expression in T helper cell subsets. Science. 1995 Nov 17;270(5239):1215–1218. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5239.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr, Stahl N., Yancopoulos G. D. STAT3 activation by cytokines utilizing gp130 and related transducers involves a secondary modification requiring an H7-sensitive kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6915–6919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe J., Rogers N. C., Witthuhn B. A., Watling D., Harpur A. G., Wilks A. F., Stark G. R., Ihle J. N., Kerr I. M. Kinase-negative mutants of JAK1 can sustain interferon-gamma-inducible gene expression but not an antiviral state. EMBO J. 1996 Feb 15;15(4):799–809. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan D., Kharbanda S. M., Ogata A., Urashima M., Frank D., Malik N., Kufe D. W., Anderson K. C. Oncostatin M induces association of Grb2 with Janus kinase JAK2 in multiple myeloma cells. J Exp Med. 1995 Dec 1;182(6):1801–1806. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.6.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danial N. N., Pernis A., Rothman P. B. Jak-STAT signaling induced by the v-abl oncogene. Science. 1995 Sep 29;269(5232):1875–1877. doi: 10.1126/science.7569929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Chen H. E., Goelz S., Larner A. C., Neel B. G. Differential regulation of the alpha/beta interferon-stimulated Jak/Stat pathway by the SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase SHPTP1. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):7050–7058. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.7050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Petricoin E., 3rd, Benjamin C., Pine R., Weber M. J., Larner A. C. Requirement for MAP kinase (ERK2) activity in interferon alpha- and interferon beta-stimulated gene expression through STAT proteins. Science. 1995 Sep 22;269(5231):1721–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.7569900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Petricoin E., 3rd, Larner A. C. Activation of protein kinase A inhibits interferon induction of the Jak/Stat pathway in U266 cells. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 1;271(9):4585–4588. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.4585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman G. M., Chuang E. J., Finbloom D. S. IgG immune complexes inhibit IFN-gamma-induced transcription of the Fc gamma RI gene in human monocytes by preventing the tyrosine phosphorylation of the p91 (Stat1) transcription factor. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 1;154(1):318–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. S., Hui C. C., Pawson T. SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase as a target of protein-tyrosine kinases. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1607–1611. doi: 10.1126/science.8096088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrer D. K., Feng G. S., Yang Y. C. Syp associates with gp130 and Janus kinase 2 in response to interleukin-11 in 3T3-L1 mouse preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 20;270(42):24826–24830. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.42.24826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guschin D., Rogers N., Briscoe J., Witthuhn B., Watling D., Horn F., Pellegrini S., Yasukawa K., Heinrich P., Stark G. R. A major role for the protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 in the JAK/STAT signal transduction pathway in response to interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 3;14(7):1421–1429. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07128.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hama N., Paliogianni F., Fessler B. J., Boumpas D. T. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II downregulates both calcineurin and protein kinase C-mediated pathways for cytokine gene transcription in human T cells. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1217–1222. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotamisligil G. S., Peraldi P., Budavari A., Ellis R., White M. F., Spiegelman B. M. IRS-1-mediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-alpha- and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Science. 1996 Feb 2;271(5249):665–668. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5249.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J., Schindler U., Henzel W. J., Ho T. C., Brasseur M., McKnight S. L. An interleukin-4-induced transcription factor: IL-4 Stat. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1701–1706. doi: 10.1126/science.8085155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Protein kinases and phosphatases: the yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90405-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N. Cytokine receptor signalling. Nature. 1995 Oct 19;377(6550):591–594. doi: 10.1038/377591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N. STATs: signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell. 1996 Feb 9;84(3):331–334. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkiv L. B. Cytokines and STATs: how can signals achieve specificity? Immunity. 1995 Jul;3(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkiv L. B., Glimcher L. H. Repression of class II major histocompatibility complex genes by cyclic AMP is mediated by conserved promoter elements. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1583–1592. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingmüller U., Lorenz U., Cantley L. C., Neel B. G., Lodish H. F. Specific recruitment of SH-PTP1 to the erythropoietin receptor causes inactivation of JAK2 and termination of proliferative signals. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleider R. J., Sugimoto S., Bennett A. M., Kashishian A. S., Cooper J. A., Shoelson S. E., Walsh C. T., Neel B. G. Activation of the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP2 by its binding site, phosphotyrosine 1009, on the human platelet-derived growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21478–21481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. X., Migone T. S., Tsang M., Friedmann M., Weatherbee J. A., Zhou L., Yamauchi A., Bloom E. T., Mietz J., John S. The role of shared receptor motifs and common Stat proteins in the generation of cytokine pleiotropy and redundancy by IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-13, and IL-15. Immunity. 1995 Apr;2(4):331–339. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrero M. B., Schieffer B., Paxton W. G., Heerdt L., Berk B. C., Delafontaine P., Bernstein K. E. Direct stimulation of Jak/STAT pathway by the angiotensin II AT1 receptor. Nature. 1995 May 18;375(6528):247–250. doi: 10.1038/375247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migone T. S., Lin J. X., Cereseto A., Mulloy J. C., O'Shea J. J., Franchini G., Leonard W. J. Constitutively activated Jak-STAT pathway in T cells transformed with HTLV-I. Science. 1995 Jul 7;269(5220):79–81. doi: 10.1126/science.7604283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nghiem P., Ollick T., Gardner P., Schulman H. Interleukin-2 transcriptional block by multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin kinase. Nature. 1994 Sep 22;371(6495):347–350. doi: 10.1038/371347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Matozaki T., Horita K., Fujioka Y., Kasuga M. Role of SH-PTP2, a protein-tyrosine phosphatase with Src homology 2 domains, in insulin-stimulated Ras activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6674–6682. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse R. N., Feinman R., Shuai K., Darnell J. E., Jr, Ravetch J. V. Interferon gamma-induced transcription of the high-affinity Fc receptor for IgG requires assembly of a complex that includes the 91-kDa subunit of transcription factor ISGF3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4314–4318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernis A., Gupta S., Gollob K. J., Garfein E., Coffman R. L., Schindler C., Rothman P. Lack of interferon gamma receptor beta chain and the prevention of interferon gamma signaling in TH1 cells. Science. 1995 Jul 14;269(5221):245–247. doi: 10.1126/science.7618088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann W. P., Graves L. M., Baumann H., Morella K. K., Gearing D. P., Nielsen M. D., Krebs E. G., Nathanson N. M. Phosphorylation of the human leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) receptor by mitogen-activated protein kinase and the regulation of LIF receptor function by heterologous receptor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5361–5365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
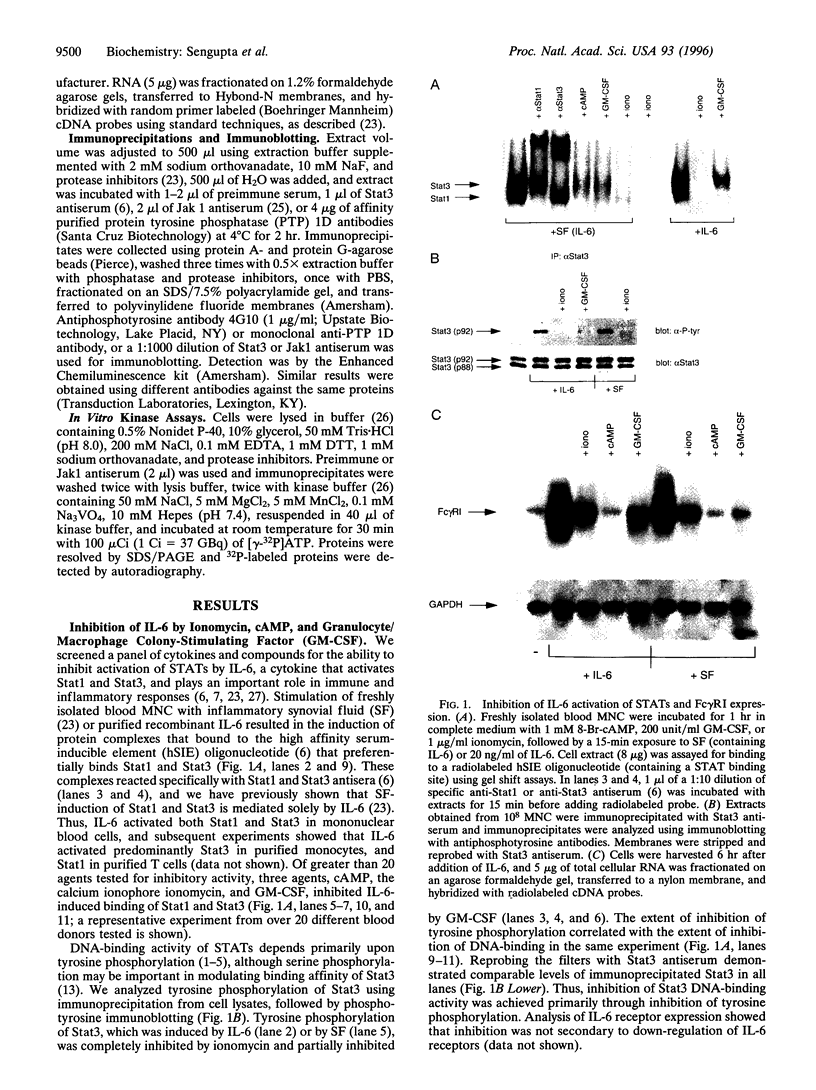
- Sengupta T. K., Chen A., Zhong Z., Darnell J. E., Jr, Ivashkiv L. B. Activation of monocyte effector genes and STAT family transcription factors by inflammatory synovial fluid is independent of interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1015–1025. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Farruggella T. J., Boulton T. G., Zhong Z., Darnell J. E., Jr, Yancopoulos G. D. Choice of STATs and other substrates specified by modular tyrosine-based motifs in cytokine receptors. Science. 1995 Mar 3;267(5202):1349–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.7871433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo S. J., Jacobson N. G., Dighe A. S., Gubler U., Murphy K. M. Developmental commitment to the Th2 lineage by extinction of IL-12 signaling. Immunity. 1995 Jun;2(6):665–675. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T. Cytokine signaling through nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):251–255. doi: 10.1126/science.7716517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauchi T., Feng G. S., Marshall M. S., Shen R., Mantel C., Pawson T., Broxmeyer H. E. The ubiquitously expressed Syp phosphatase interacts with c-kit and Grb2 in hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):25206–25211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W., Lammers R., Huang J., Ullrich A. Activation of a phosphotyrosine phosphatase by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1611–1614. doi: 10.1126/science.7681217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
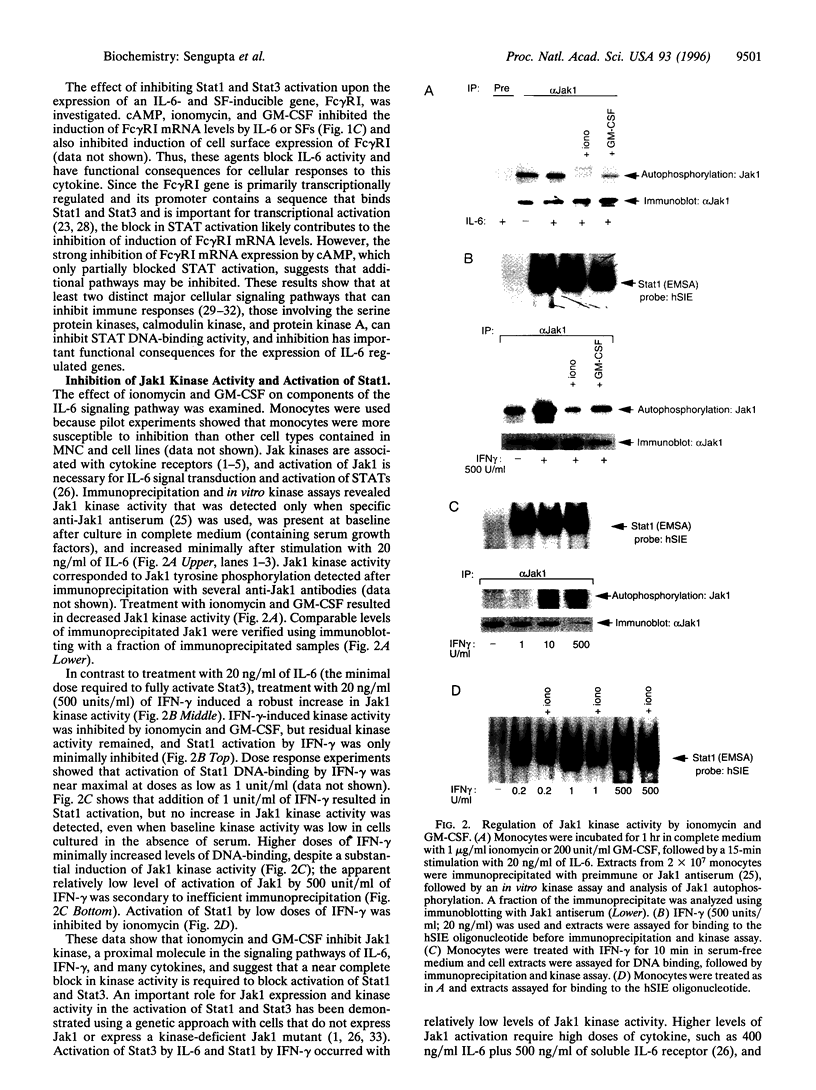
- Wang F., Sengupta T. K., Zhong Z., Ivashkiv L. B. Regulation of the balance of cytokine production and the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) transcription factor activity by cytokines and inflammatory synovial fluids. J Exp Med. 1995 Dec 1;182(6):1825–1831. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.6.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen Z., Zhong Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Maximal activation of transcription by Stat1 and Stat3 requires both tyrosine and serine phosphorylation. Cell. 1995 Jul 28;82(2):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90311-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F., Harpur A. G., Kurban R. R., Ralph S. J., Zürcher G., Ziemiecki A. Two novel protein-tyrosine kinases, each with a second phosphotransferase-related catalytic domain, define a new class of protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2057–2065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin T., Tsang M. L., Yang Y. C. JAK1 kinase forms complexes with interleukin-4 receptor and 4PS/insulin receptor substrate-1-like protein and is activated by interleukin-4 and interleukin-9 in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26614–26617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. L., Meyer D. J., Campbell G. S., Larner A. C., Carter-Su C., Schwartz J., Jove R. Enhanced DNA-binding activity of a Stat3-related protein in cells transformed by the Src oncoprotein. Science. 1995 Jul 7;269(5220):81–83. doi: 10.1126/science.7541555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Wegenka U. M., Lütticken C., Buschmann J., Decker T., Schindler C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. The signalling pathways of interleukin-6 and gamma interferon converge by the activation of different transcription factors which bind to common responsive DNA elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1657–1668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
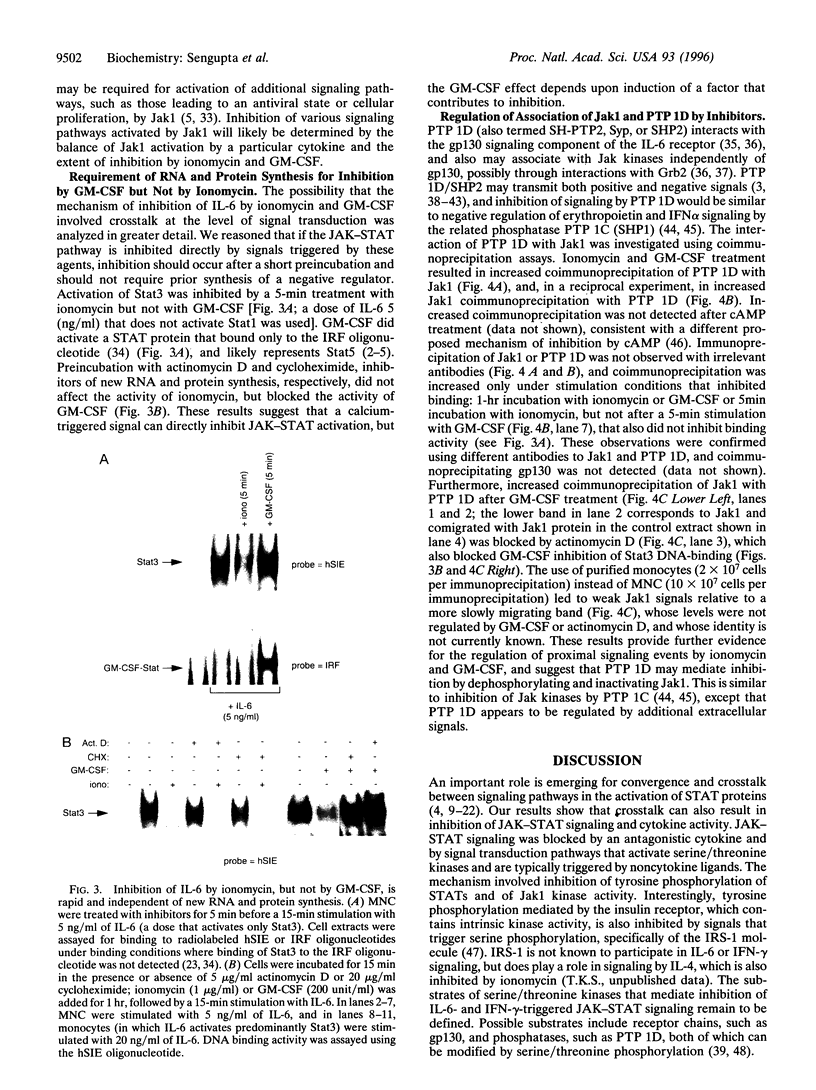
- Zhang X., Blenis J., Li H. C., Schindler C., Chen-Kiang S. Requirement of serine phosphorylation for formation of STAT-promoter complexes. Science. 1995 Mar 31;267(5206):1990–1994. doi: 10.1126/science.7701321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):95–98. doi: 10.1126/science.8140422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]