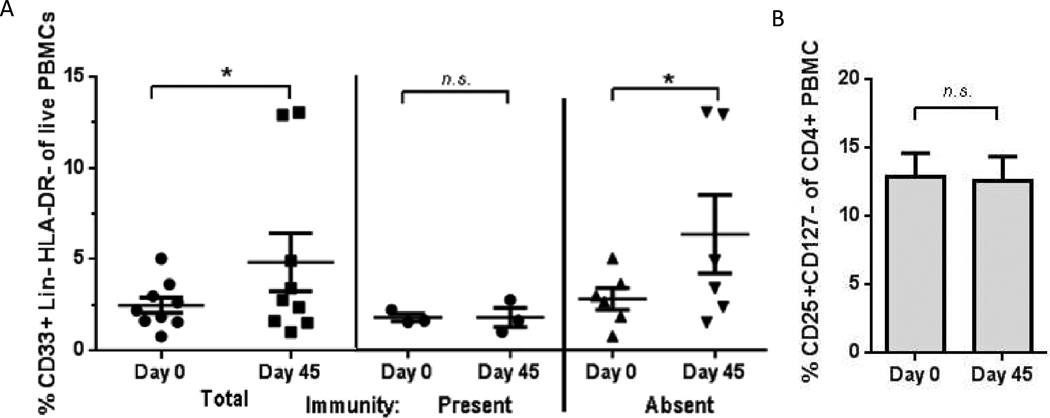
Figure 5.
A. MDSCs increased from baseline (day 0) to next consecutive evaluation (day 45). MDSCs may have contributed to failure to achieve an IFN-γ response to vaccine antigen. Fraction CD33+ of Lin-DR- were analyzed by flow cytometry. Remaining patients were not evaluable due to poor cell viability, sample not collected, or death.
Bars: mean ± standard error. * p < 0.05, Wilcoxon signed rank test. n.s. = not significant. For pairing, Spearman r2 = 0.94.
B. Peripheral T-regulatory cells did not appreciably decrease from baseline (day 0) to next consecutive evaluation (day 45), despite single bolus of intravenous cyclophosphamide. n = 8. Fraction CD25+CD127- of CD4+ were analyzed by flow cytometry. Remaining patients were not evaluable due to poor cell viability, sample not collected, or death.
Bars: mean ± standard error. n.s. = not significant, Wilcoxon signed rank test. For pairing, Spearman r2 = 1.0.