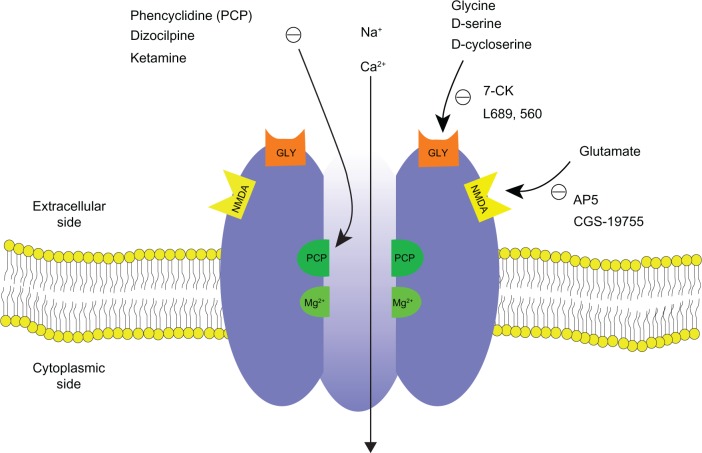
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of NMDA receptor complex. The NMDA receptor is an ionotropic glutamate receptor for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function.47,49 Glutamate (and NMDA) binds to the agonist site on the NMDA receptors. PCP, ketamine, and dizocilpine bind to the PCP receptor in the inside of the NMDA receptors. Glycine and D-serine bind to a glycine modulatory site on the NMDA receptors. The NMDA receptor is blocked by Mg2+ in a voltage sensitive manner. Activation of NMDA receptor by binding of both glutamate and glycine results in the opening of the channel. This allows voltage-dependent flow of Na+ and small amounts of Ca2+ ions into the cell and K+ out of the cell. The symbol (−) denotes inhibitory effect.
Abbreviations: NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; 7-CK, 7-chlorokynurenic acid; L689,560, trans-2-carboxy-5,7-dichloro-4-phenylaminocarbonyl; AP5, 2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid; CGS-19775, cis-4-phosphonomethyl-2-piperidinecarboxylic acid.