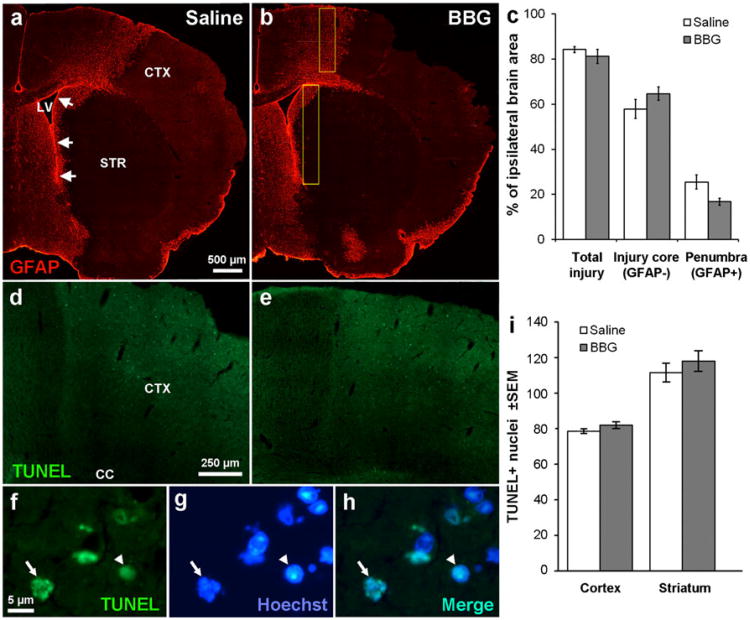
Fig. 5.
P2X7 inhibition is not neuroprotective after stroke. a MCAO in C57BL/6 mice caused severe loss of cells as shown in the lack of GFAP immunofluorescent staining in the injury core, involving both the striatum (STR) and cortex (CTX). The medial penumbra towards the SVZ (arrows) and neighboring lateral ventricle (LV) shows abundant GFAP+staining. b The injury appeared similar in mice treated for 3 days with BBG. c Measurements of the injury area were calculated as a percentage of the whole ipsilateral brain and show no significant effect of a BBG treatment over 3 days following MCAO on the area of the injured core or the penumbra. N=6 saline, 4 BBG. TUNEL staining shows many apoptotic cells in the penumbral region of the cortex in both saline- (d) and BBG (e)-injected mice after MCAO. Apoptotic nuclei were defined by TUNEL staining (f) and their typical condensed (arrowhead) or fragmented (arrow) appearance as seen in Hoechst staining (g) as confirmed by double staining (h). i Apoptotic cells were counted in the primary somatosensory area and medial striatum (yellow boxes in b) with a 63× oil objective and were not significantly different between vehicle and BBG-treated mice. N=5 saline, 4 BBG