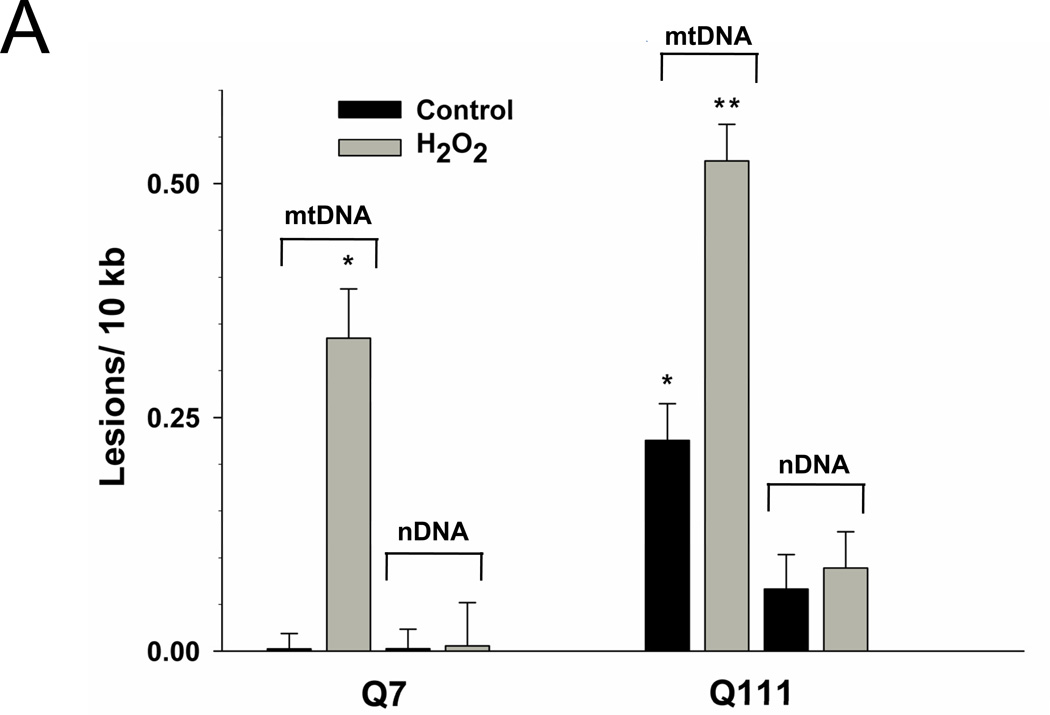
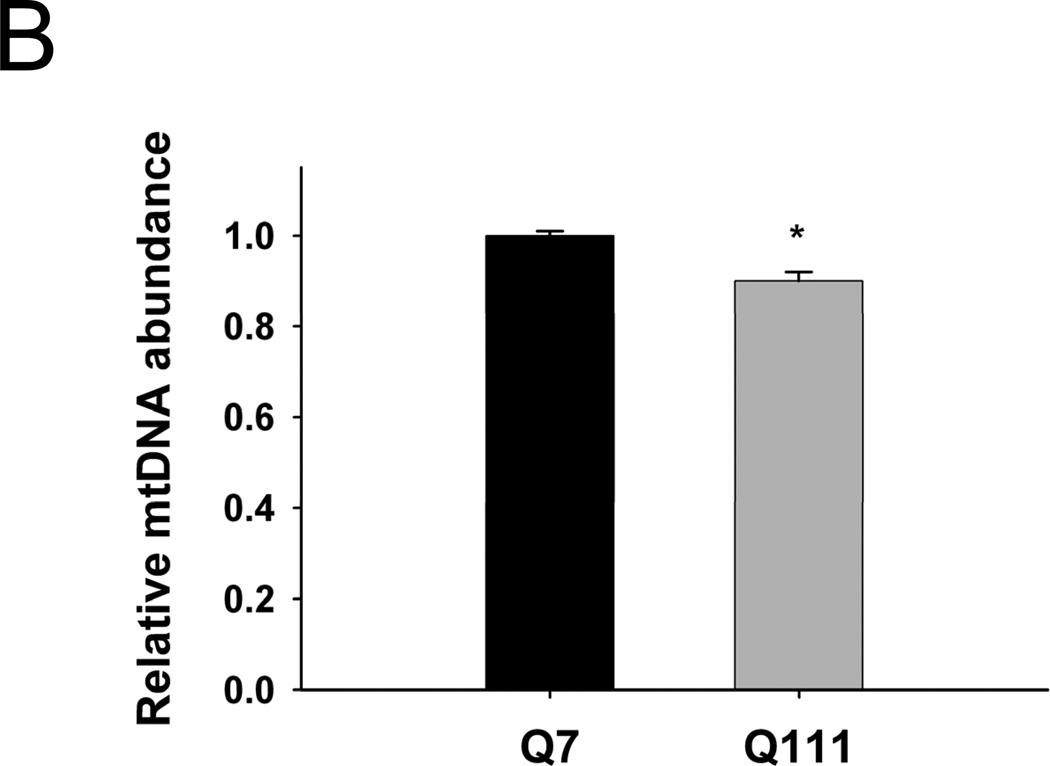
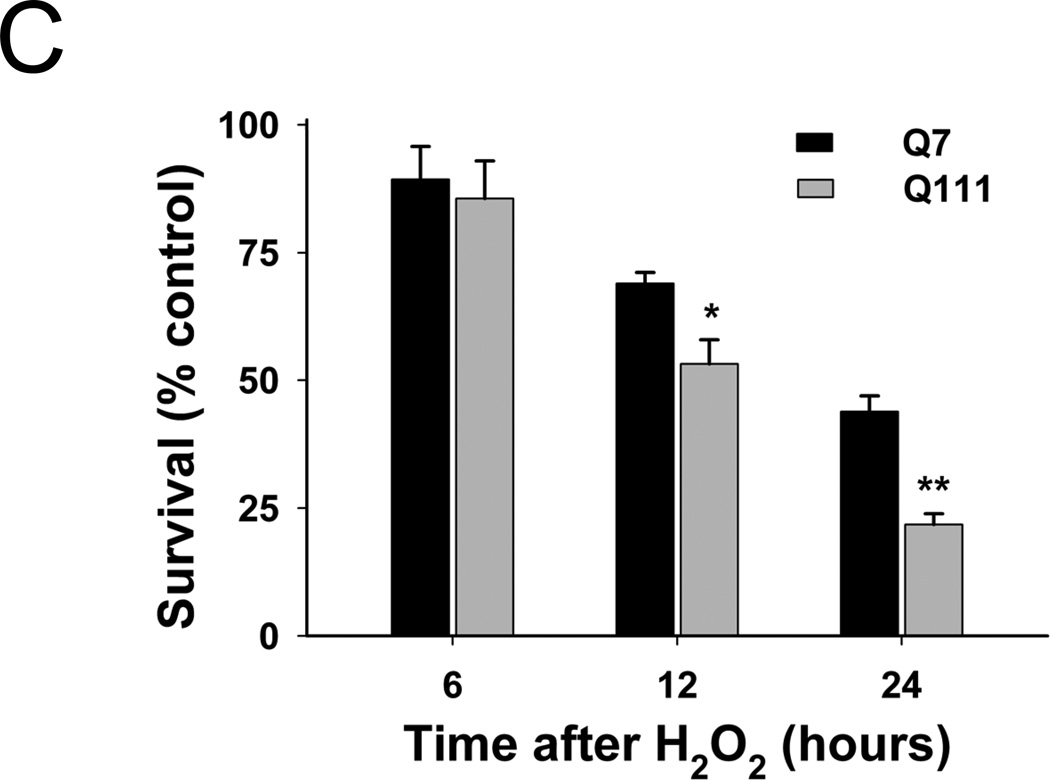
Fig. 2.
Mutant Q111 cells exhibit higher basal levels of mtDNA damage and are more sensitive to H2O2 treatment than wild type Q7 cells. (A) Cells were treated with 200 µM H2O2 and DNA isolated 3 hours after treatment. Frequency of mtDNA and nDNA lesions per 10 kb per strand after normalization for changes in mtDNA abundance. n=3 independent experiments and 3 QPCR analyses. *p<0.001 versus Q7 control and **p<0.001 versus Q111 control. (B) Relative abundance of mtDNA molecules. *p<0.01 versus Q7. n=6 independent experiments. (C) Cells were treated with 200 µM H2O2 and cell viability was determined after 6, 12, and 24 hours of treatment using the trypan blue exclusion method. Results are expressed as % of control. *p=0.02 and **p<0.001 versus WT Q7 cells. n=2−3 independent experiments in duplicate.