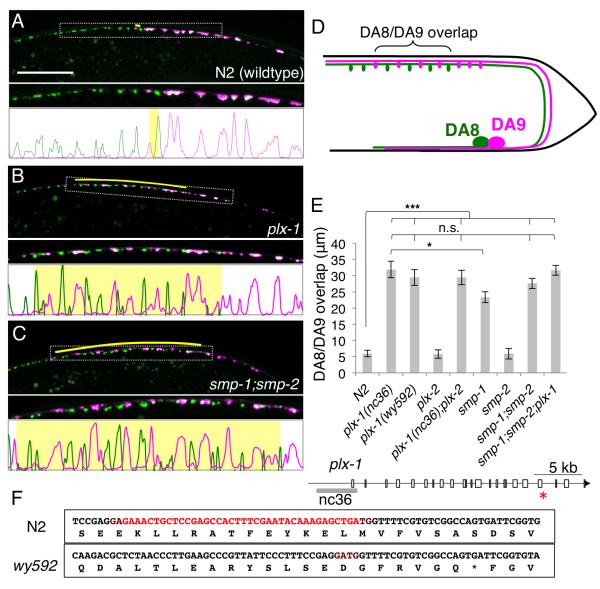
Figure 2. plexin and semaphorin mutants have synaptic tiling defects.
(A-C) Synaptic tiling defect in L4 animals of wildtype (A) plx-1(nc36) (B) and smp-1;smp-2 (C) mutants. Overlap between the DA8 and DA9 synaptic domains are indicated in yellow bars. Magnified images (represented by dotted boxes) and line-scan images within the magnified region were also shown. (D) Schematic representation of the tiling mutant phenotype. (E) Quantification of overlap between DA8/DA9 synaptic domains. Error bars; standard error of mean. Triple asterisks; p<0.001, Single asterisk; p<0.05 n.s.: not significant (ANOVA/Tukey-HSD). (F) Schematic representation of the genomic locus of the plx-1 gene. White boxes represent exons. The grey bar represents the deletion in nc36. The res asterisk indicates the position of deletion found in wy592 allele. DNA and corresponding amino acid sequences around the deletion found in wy592 of wildtype and wy592 are shown in the boxes. Sequence deleted in wy592 allele is shown in red. See also Figure S1 to S4.