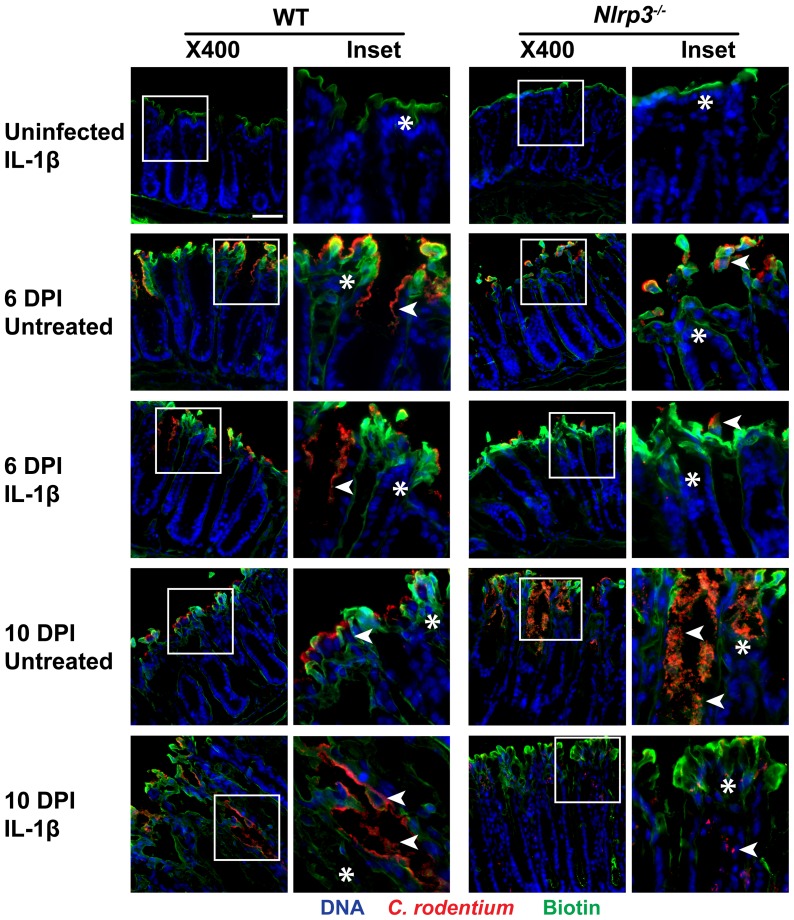
Figure 2. IL-1β treatments modulate C. rodentium penetration and epithelial integrity.
Biotin was administered into the lumen of the distal colon at 6 or 10 DPI. Cryosections were stained and viewed under fluorescent microscopy for C. rodentium infiltration (in red; indicated by arrowheads in the enlarged image of the inset highlighted by boxes in the left panels) and biotin penetration (green; indicated by asterisks). Uninfected IL-1β-treated mice retained biotin to the apical surface. In non-treated mice at 6 DPI, the bacterial infiltration and biotin penetration was increased. IL-1β treatments at 6 DPI did not seem to have a major effect on infiltration or epithelial integrity. In non-treated mice at 10 DPI, the bacterial infiltration and epithelial barrier disruption were lowered in WT and elevated in Nlrp3−/− mice, relative to 6 DPI. In IL-1β-treated mice at 10 DPI, the bacterial infiltration and barrier disruption were elevated in WT and lowered in Nlrp3−/− mice. Bacterial colonization followed the same trend as biotin penetration. Magnification X400, bar 50 µm.