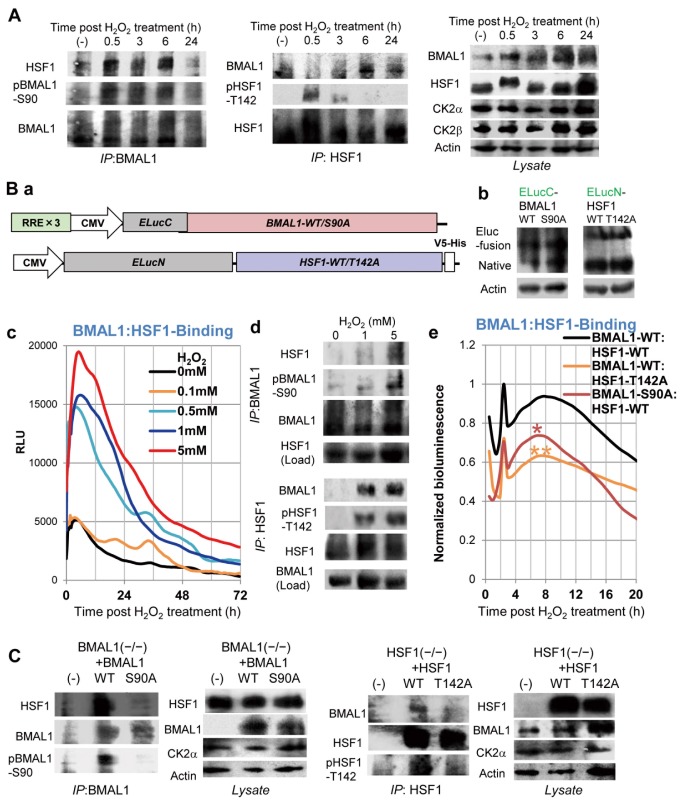
Figure 3. CK2-mediated phosphorylation regulates BMAL1-HSF1 binding.
(A) WT MEFs were cOS-pulsed. At the indicated time, BMAL1- and HSF-IP and lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for BMAL1, phospho-BMAL1-S90 (pBMAL1-S90), HSF1, phospho-HSF1-T142 (pHSF1-T142), CK2alpha, CK2beta, and actin. Representative images are shown (n = 3). (B) CK2 regulates BMAL1-HSF1 binding in living cells. U2OS cells transiently expressing ELucN-HSF1 (WT or T142A lacking a CK2-phospholylation site) and ELucC-BMAL1 (WT or S90A lacking a CK2-phospholylation site) (a; construction map, b; immunoblot detection of recombinant and native proteins) were analyzed by real-time split luciferase complementation assay to detect binding between BMAL1 and HSF1. Relative bioluminescence profiles (n = 4) reveal H2O2 (treated for 10 min) dose-dependent BMAL1-HSF1 binding (c). BMAL1- and HSF-IP and lysates of U2OS cells after H2O2 (0, 1, 5 mM) treatment (0.5 h for HSF1-IP or, 4 h for BMAL1-IP) were analyzed by immunoblotting for BMAL1, pBMAL1-S90, HSF1, and pHSF1-T142. Representative images are shown (n = 3) (d). Normalized profiles (n = 4) show a significant difference between WT and the mutants: ⋆ (P<0.05); ⋆⋆ (P< 0.01); at 8 h post cOS-pulse (e). (C) BMAL1−/− MEFs harboring BMAL1-WT or BMAL1-S90A and HSF1−/− MEFs harboring HSF1-WT or HSF1-T142A were cOS-pulsed. At 3 h (30 min for P-HSF1-T142 and P-BMAL1-S90 detection), HSF- and BMAL1-IP and lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. Representative images are shown (n = 3).