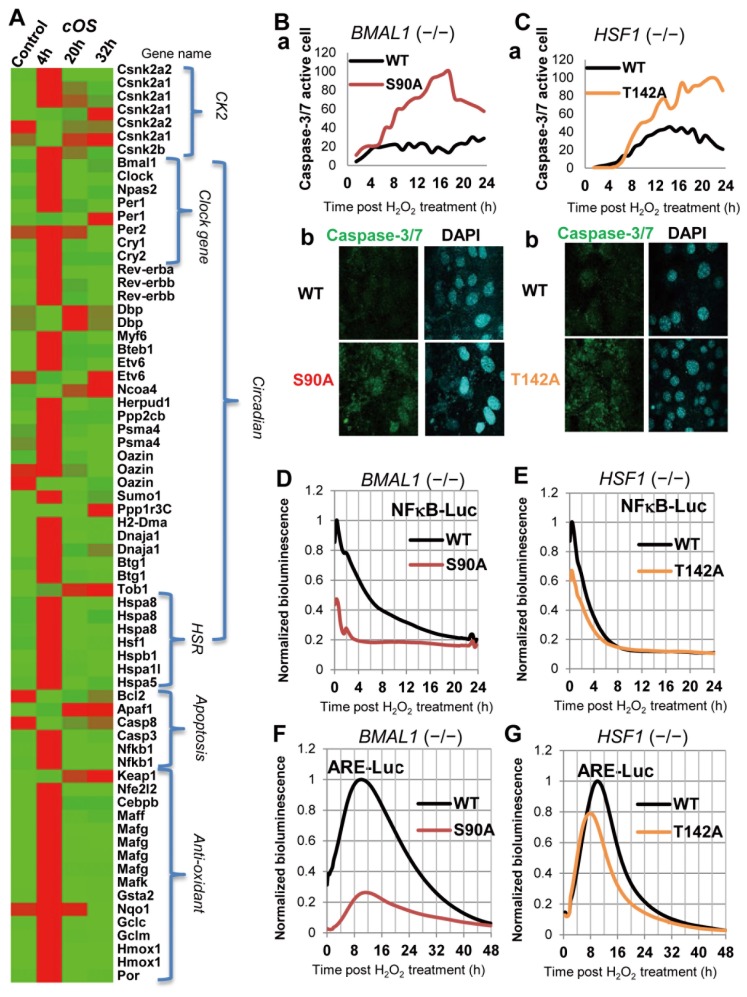
Figure 6. cOS-responsive circadian transcriptome regulated by CK2-signaling.
(A) Expression profile of the core cOS-evoked circadian transcriptome for cell survival. Microarray analysis was performed to profile regulated genes in NIH-3T3:Per2-Luc with/without cOS-pulse. Functionally relevant genes for cOS-evoked responses were listed by annotation clustering and exploring biological pathways. A heatmap of the cOS-responsive genes encoding CK2, circadian, HSR, apoptosis, and anti-oxidant–related proteins is shown. Gradient representation from brightest red to brightest green indicates relatively high to low levels of gene expression. The values for the heatmap are shown in Table S2. (B-G) CK2-mediated BMAL1/HSF1 phosphorylation regulates anti-apoptotic/oxidant pathways after cOS-pulse. BMAL1−/− MEFs harboring BMAL1-WT or BMAL1-S90A (B,D,F) and HSF1−/− MEFs harboring HSF1-WT or HSF1-T142A (C,E,G) were cOS-pulsed. (B,C) (a) Normalized profiles for caspase-3/7-active cell numbers as monitored by live cell time-lapse imaging using CellEvent™ Caspase-3/7 Green (Movie S3 and S4). (b) Representative confocal images of fixed cells with DAPI-visualized nuclei post cOS-pulse are shown. (D,E) Cells transiently expressing NF-kappa-B-driven Luc were cOS-pulsed. Normalized profiles of NF-kappa-B-Luc are shown (n = 4). (F,G) Cells transiently expressing ARE-Luc, the Nrf2-mediated anti-oxidant reporter, were cOS-pulsed. Normalized profiles of ARE-Luc are shown (n = 4).